Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
During a total solar eclipse the moon almost entirely covers the sphere of the sun. Write the relation between the distances and sizes of the sun and moon.
उत्तर
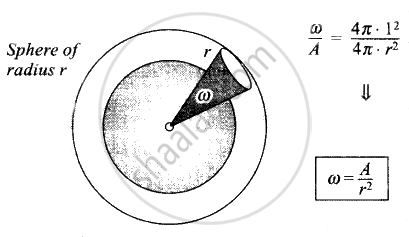
In geometry, a solid angle (symbol: Ω or w) is the twodimensional angle in three-dimensional space that an object subtends at a point. It is a measure of how large the object appears to an observer looking from that point. In the International System of Units (SI), a solid angle is expressed in a dimensionless unit called a steradian (symbol: sr)
Solid Angle
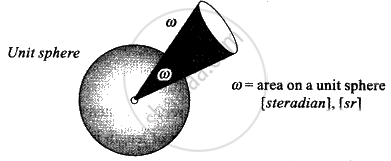
A small object nearby may subtend the same solid angle as a larger object farther away. For example, although the Moon is much smaller than the Sun, it is also much closer to Earth.
The diagram given below shows that the moon almost entirely covers the sphere of the sun.
Rme = Distance of moon from earth
Rse = Distance of sun from the earth
Let the solid angle made by the sun and moon is dΩ, we can write
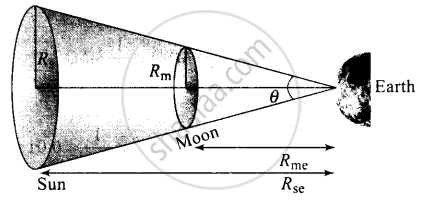
dΩ = `A_(sun)/R_(se)^2 = A_("moon")/R_(me)^2`
Here, Asun = Area of the sun
Amoon = Area of the moon
⇒ θ = `(πR_s^2)/(R_(se)^2) = (πR_m^2)/(R_(me)^2)`
⇒ `(R_s/R_(se))^2 = (R_m/R_(me))^2`
⇒ `R_s/R_(se) = R_m/R_(me)` or `R_s/R_m = R_(se)/R_(me)`
(Here, radius of the sun and moon represent their sizes respectively)
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The volume of a cube of side 1 cm is equal to ______ m3
A vehicle moving with a speed of 18 km h–1covers ______ m in 1 s.
A famous relation in physics relates ‘moving mass’ m to the ‘rest mass’ m0 of a particle in terms of its speed v and the speed of light, c. (This relation first arose as a consequence of special relativity due to Albert Einstein). A boy recalls the relation almost correctly but forgets where to put the constant c. He writes:
`m = m_0/(1-v^2)^(1/2)`
Guess where to put the missing c.
Fill in the blank by suitable conversion of unit:
1 kg m2s–2= ______ g cm2 s–2
Fill in the blank by suitable conversion of unit:
1 m =______ ly
Fill in the blank by suitable conversion of unit:
3.0 m s–2= ______ km h–2
Fill in the blank by suitable conversion of unit:
G= 6.67 × 10–11 N m2 (kg)–2= ______ (cm)3s–2 g–1
In which of the following systems can scientific data be exchanged between different parts of the world?
If the unit of force is 100 N, unit of length is 10 m and unit of time is 100 s, what is the unit of mass in this system of units?
A new system of units is proposed in which unit of mass is α kg, unit of length β m and unit of time γ s. How much will 5 J measure in this new system?
