Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain the condition of consumer's equilibrium with the help of utility analysis.
उत्तर
Given the price of the good, a consumer will decide the amount of goods to buy. So, the consumer compares the price of the good with its utility. A rational consumer will be at equilibrium only when the marginal utility is equal to the price paid for the good.
MUX = PX
The marginal utility is greater than the price paid for the good, i.e. MUX > PX implies that the consumer is not in equilibrium and buys more of a good. While the marginal utility is lesser than the price paid for the good, i.e. MUX < PX implies that the consumer is not in equilibrium and buys less of that good.
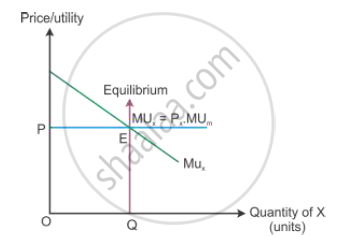
In the diagram, OP is the price of the good given on the Y-axis and OQ is the utility given on the X-axis. The marginal utility curve MUX slopes downwards because the marginal utility diminishes with every additional consumption of X. The consumer reaches equilibrium at Point E, where the marginal utility is equal to the price paid for the good.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A consumer consumes only two goods. Explain consumer's equilibrium with the help of utility analysis.
A consumer consumes only two goods X and Y. Marginal utilities of X and Y is 3 and 4 respectively. Prices of X and Y are Rs 4 per unit each. Is consumer in equilibrium? What will be further reaction of the consumer? Give reasons.
A consumer consumes only two goods X and Y. Marginal utilities of X and Y are 4 and 3 respectively. Price of X and price of Y is Rs 3 per unit. Is consumer in equilibrium? What will be further reaction of the consumer? Give reasons.
A consumer consumes only two goods X and Y. The marginal utilities of X and of Y is 3. Prices of X and Y are Rs 2 and Rs 1 respectively. Is consumer in equilibrium? What will be further reaction of the consumer?
Give reasons.
A consumer consumes only two goods X and Y. If marginal utilities of X and Y are 4 and 5 respectively, and if price of X is Rs 5 per unit and that of Y is Rs 4 per unit is the consumer in equilibrium? What will be further reaction of the consumer? Explain.
A consumer consumes only two goods X and Y. Marginal utility of each is 2. The price per unit of X and Y is Re 1 and Rs 2 respectively. Is the consumer in equilibrium? What will be the further reaction of the consumer? Explain.
A consumer consumes only two goods X and Y and is in equilibrium. Price of X falls. Explain the reaction of the consumer through the Utility Analysis.
Should the following be treated as final expenditure or intermediate expenditure? Give reasons for your answer.
(i) Purchase of furniture by a firm.
(ii) Expenditure on maintenance by a firm.
What is meant by producer’s equilibrium? Explain the conditions of producer’s equilibrium through the ‘total revenue and total cost’ approach. Use diagram.
Answer the following question.
Explain with the help of a diagram the consumer’s equilibrium through utility approach.
"For a consumer to be in the equilibrium position, a marginal rate of substitution between the two goods must be equal to the ratio of prices of the two goods." Do you agree with the given statement? Justify your answer.
