Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain different elements of cost.
What are the elements of cost?
Name any two basic elements of cost. Give an example of each.
Explain briefly the various elements of cost.
Explain the elements of total cost.
उत्तर १
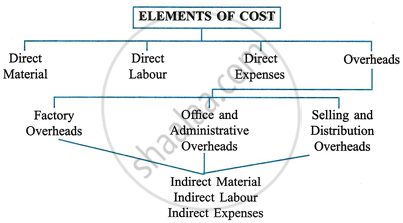
There are broadly four elements of cost:
- Materials: The substance from which a product is made is known as a material. It may be in a raw or manufactured state. The cotton, used in manufacturing cloth, sugarcane used in producing sugar, rubber, and leather, used in producing shoes, are examples of materials. Material can be direct or indirect.
- Direct material: All material that becomes an integral part of the finished product and which can be conveniently assigned to specific physical units of the finished product is known as direct material or process material. The wood used in making furniture, sugarcane in a sugar mill, raw cotton in a textile mill, and crude oil used in making diesel are examples of direct materials.
- Indirect material: All material which is used for ancillary purposes and which cannot be conveniently assigned to specific physical units is known as indirect material. Consumable stores, oil lubricants and cotton waste, printing and stationery material, nails, glue and polish used in making furniture, etc., are a few examples of indirect material. Such material may be used in the factory, office or selling and distribution division.
- Labour: Labour means the human effort required for converting materials into finished goods. It can be direct as well as indirect.
- Direct labour: Labour which takes an active and direct part in the production of a particular commodity is known as direct labour. Direct labour costs are specifically and conveniently traceable to specific products. Direct labour is also known as productive or operating labour. Wages paid to carpenters in a furniture workshop are direct labour.
- Indirect labour: Labour employed for the purpose of carrying out tasks incidental to goods produced or services provided is indirect labour. Such labour does not alter the composition, construction or condition of the product. It cannot be easily traced to specific units of output. Wages of storekeepers, timekeepers and watchmen, salesmen's salaries, directors' fees, etc., are examples of indirect labour costs.
- Expenses: Expenses may be direct or indirect.
- Direct expenses: These are the expenses that can be directly, conveniently and wholly allocated to specific cost centres or cost units. Rent paid for hire of a special machine required for a particular contract, the cost of defective work incurred in connection with a particular job, fees paid to the architect of a building, etc., are examples of direct expenses. These are also known as chargeable expenses.
- Indirect expenses: These are the expenses which cannot be directly, conveniently and wholly traced to a particular product. Rent, lighting, insurance charges, depreciation, etc., are examples of indirect expenses.
- Overheads: The term 'overhead' includes indirect material, indirect labour and indirect expenses. In other words, all indirect costs are overheads. Overheads include material and labour.
Overheads are classified as:- Production or manufacturing overheads
- Administrative overheads
- Selling Overheads
- Distribution Overheads
- Research and development Overheads
उत्तर २
There are four broad elements of cost.
- Materials: The substance from which a product is made is known as a material. It may be in a raw or manufactured state. Cotton, used in manufacturing cloth; sugarcane, used in producing sugar; rubber; and leather, used in producing shoes, are examples of materials. Material can be direct or indirect.
- Labour: Labour means the human effort required for converting materials into finished goods. It can be direct as well as indirect. For example, the wages paid to workers employed in a sugar mill.
- Expenses: Expenses may be direct or indirect.
- Overheads: The term 'overhead' includes indirect material, indirect labour and indirect expenses.
Notes
Students should refer to the answers according to their questions and preferred marks.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Write a short note on direct labour cost.
Write short note on indirect labour cost.
Costs incurred other than on material and labour for production and distribution are called ______.
Name and give examples of any two types of Overheads.
______ means amount spent on production or to provide services.
To control costs, it is essential to keep control on ______.
Which of the following is overhead cost?
Overhead is actually the total of ______.
Which of the following is related to office and administrative overheads?
Expenses may be direct or ______.
What do you mean by the term Overheads?
What consist of indirect material, indirect labour, and indirect expenses?
Overhead refers to ______.
In element-wise classification of overheads, which one of the following is not included in?
What is Indirect Labour Cost?
What are indirect expenses?
Explain the following:
Material Cost
