Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain the events up to double fertilisation after the pollen tube enters one of the synergids in an ovule of an angiosperm.
उत्तर
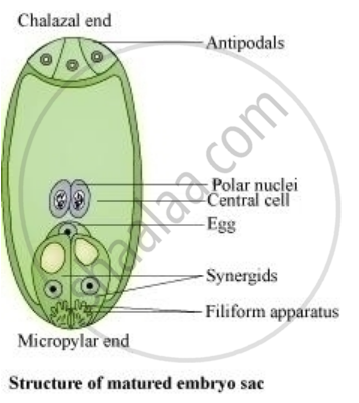
The events which occur during double fertilization are:
Two male gametes are released by the pollen tube into the cytoplasm of synergid.
One of these male gametes moves towards the egg cell and fuses with the nucleus. This process is called syngamy and results in the formation of a diploid cell, zygote, which eventually forms an embryo.
The other male gamete moves towards the polar nuclei located in the central cell and fuses with them to form a triploid primary endosperm nucleus (PEN). This process is called triple fusion.
Since two types of fusion, syngamy and triple fusion, take place here, the phenomenon is called double fertilisation.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Differentiate between outbreeding and outcrossing.
What happens to the following after fertilization?
Ovules
What happens to the following after fertilization?
Stamens
What are the advantages of the following in the flower to the plant concerned?
Protruding and easily movable anthers
What is the function of the pollen tube? Explain it with the help of a diagram.
What is the significance of the dispersal of seeds? Give any two points.
What is a fruit?
Long Answer Question:
Draw a labeled diagram of the L.S. of anatropous ovule and list the components of the embryo sac and mention their fate after fertilization.
The seed is a fertilized _______.
Syngamy results in the formation of ______.
Male gametes in angiosperms are formed by the division of ______.
What is polyembryony? How it can commercially exploited.
‘Pollination in Gymnosperms is different from Angiosperms’ – Give reasons.
Which of the following is the CORRECT sequence of events during double fertilization in Angiosperms?
By which of the following the megasporangium proper of an angiosperm ovule is represented?
By which of the following double fertilization is exhibited?
Double fertilization is fusion of ______.
Fusion of one of the male gametes with egg nucleus is referred to as ______.
______ have the smallest seeds in the plant kingdom.
Which is the triploid tissue in a fertilised ovule? How is the triploid condition achieved?
