Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain how price is determined in a perfectly competitive market with fixed number of firms.
उत्तर
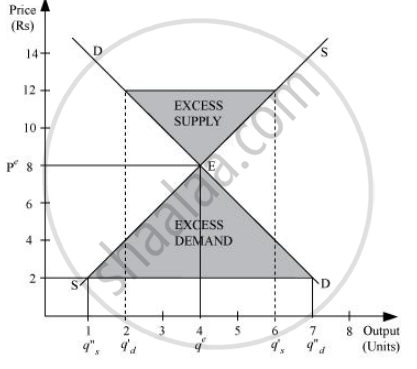
When the number of firms in a perfectly competitive market is fixed, the firms are operating in the short-run. The equilibrium price is determined by the intersection of market demand curve and supply curve. It is the price at which the market demand equals market supply.
In the given figure, if at any price above Pe, let us say Rs 12, there will be an excess supply, which will increase the competition among the sellers and they will reduce the price in order to sell more output. This causes a fall in the price, finally to Rs 8 (Pe), where the demand equals supply.
If at any price lower than Pe , let us say Rs 2, there will be an excess demand that will raise the competition among the buyers or consumers and they will be ready to pay higher price for the given output. This will increase the price to Rs 8 (equilibrium price), where the market will reach the equilibrium.
Thus, the invisible hands of market operate automatically whenever there exist excess demand and excess supply; ensuring equilibrium in the market.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Explain ‘large number of buyers and sellers' features of a perfectly competitive market.
What is a price taker firm?
Explain the implications of the following : Perfect knowledge in perfect competition.
Explain Perfect knowledge about the markets feature of perfect competition.
Under what market condition does Average Revenue always equal Marginal Revenue? Explain.
There are no barriers in the way of firms leaving or joining industry in a perfectly competitive market. Explain the significance of this feature.
Why can a firm not earn abnormal profits under perfect competition in the long run? Explain.
Explain the implication of ‘freedom of entry and exit to the firms’ under perfect competition.
In which market form can a firm not influence the price of the product?
What are the characteristics of a perfectly competitive market?
How is the optimal amount of labour determined in a perfectly competitive market?
Answer the following question.
Is a firm under perfect competition a price taker, or a price maker? Justify your answer.
Choose the correct answer from given options
A firm is not a price maker under
Under Perfect Competition, a firm will enjoy normal profit in the long run even if it enjoys supernormal profit in the short run. Explain.
Explain the short-run equilibrium of a firm facing losses under Perfect Competition.
How is Total Revenue under perfect competition different from Total Revenue under imperfect competition? Give two points to show the difference.
