Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain intragenic and intergenic interaction with the help of example.
उत्तर
- Intragenic interactions:
These types of interactions occur between the alleles of the same gene. e.g. Incomplete dominance, codominance, and multiple allele series of a gene.
Incomplete dominance:
- Incomplete dominance is a deviation of Mendel’s law of dominance.
- In incomplete dominance, both the alleles (genes) of an allelomorphic pair express themselves partially.
- One allele (gene) cannot suppress the expression of the other allele (gene) completely.
- In such a case, there is an intermediate expression in the F1 hybrid.
- In Mirabilis jalapa, if a red-flowered (RR) plant is crossed with a white-flowered (RR) plant, then F1 offsprings have pink (Rr) flowers.

Phenotypic ratio → 1 : 2 : 1 (1 Red : 2 Pink : 1 White)
Genotypic ratio → 1 : 2 : 1 (1 RR : 2 Rr : 1 rr)
Co-dominance
- Coat colour in cattle is a classic example of co-dominance.
- There are two types, one with a red coat (skin with red colour hair) and the other with a white coat (with white hair).
- When red cattle (RR) is crossed with white cattle (WW), F1 hybrids (RW) have roan colour. Roans have a mixture of red and white colour hair.
- Thus, both traits are expressed equally. In F2 generation (produced by interbreeding of roans), red (RR), roans (RW) and white (WW) are produced in the ratio 1: 2: 1.
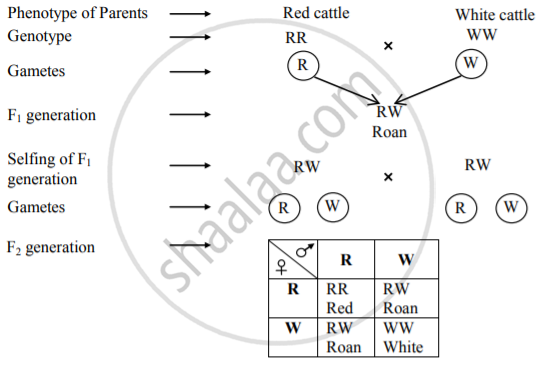
Phenotypic ratio → 1 : 2 : 1 (1 Red coat : 2 Roan : 1 White coat)
Genotypic ratio → 1 : 2 : 1 (1 RR : 2 RW : 1 WW)
2. Intergenic interaction:
These types of interactions occur between the alleles of different genes present on the same or different chromosomes. e.g. Pleiotropy, polygenes, epistasis, supplementary and complementary genes, etc.
- When a single gene controls two (or more) different traits it is called pleiotropic gene and the phenomenon is called pleiotropy or pleiotropism.
- The phenotypic ratio is 1: 2 instead of 3: 1 because of the death of recessive homozygote.
- For example, the disease, sickle cell anaemia is caused by the gene HbS. The normal or healthy gene is HbA and is dominant.
- The carriers (heterozygotes – HbA /HbS) show signs of mild anaemia as their RBCs become sickle-shaped (half-moon shaped) in oxygen deficiency. They are said to have the sickle-cell trait and are normal in normal conditions.
- The homozygotes with recessive gene HbS however, die of fatal anaemia.
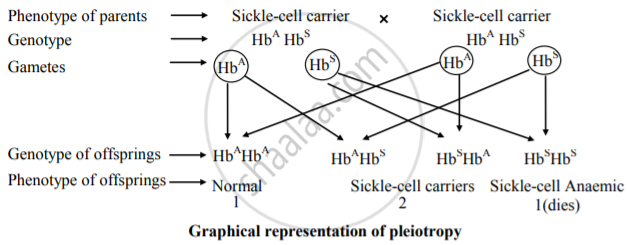
A marriage between two carriers will produce normal, carriers and sickle-cell anaemic children in a 1: 2: 1 ratio.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Why the ratio in pleiotropy is 2 : 1? Explain it with an example.
_______________ is interaction between two alleles which are present on the same gene locus of two homologous chromosomes.
Sickle cell anaemia can be lethal in ____________ condition.
______ is an example of pleiotropy.
In ____________, one could get same genotypic and phenotypic ratio.
Assertion (A): In Mirabilis jalapa (4 o'clock plant), a cross between Red flowered plant and White-flowered plant (both homozygous) produced Pink flowered plant in F1 generation.
Reason (R): In this plant, flower colour is controlled by pleiotropic genes
______ represents the genotype of a carrier carrying a gene for sickle-cell anaemia.
Explain the law of dominance and compare how it differs from incomplete dominance and co-dominance.
If a red flowered Mirabilis jalapa plant is crossed with a white flowered plant, what will be the phenotypic ratio in F2 generation? Show it by a chart.
A pea plant homozygous for yellow round seed is crossed with its recessive parents. Calculate the phenotypic and genotypic ratio with the help of a checkerboard.
