Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain national income equilibrium through aggregate demand and aggregate supply. Use diagram. Also explain the changes that take place in an economy when the economy is not in equilibrium
उत्तर
Aggregate demand and aggregate supply approach (AD and AS approach) Equilibrium level of income are attained only when aggregate demand is equal to aggregate supply. It is the level of output where producers plan to produce the amount of good is equal to consumers plan to purchase the amount of good. Thus, equilibrium is struck where planned output (AS) is equal to planned expenditure (AD) during a period of time.

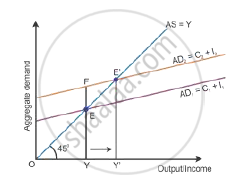
Deficient demand occurs in a situation when the aggregate demand is short of the aggregate supply corresponding to full employment in the economy. It leads to a fall in the general price level and results in deflation, i.e. AD < AS. Aggregate demand is shown by the AD curve and aggregate supply is shown by the AS curve (as shown in the diagram below). While the aggregate demand curve and the aggregate supply curve intersect each other, the full employment equilibrium is attained at Point E. OY is the full employment level of output, and EY is the aggregate demand at full employment level of output. If the aggregate demand decreases below the full employment level of output from EY to CY, then the economy will have deficient demand, (EY − CY = EC).
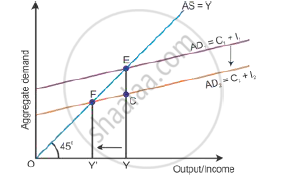
Excess demand occurs in a situation when aggregate demand is more than aggregate supply corresponding to full employment. It leads to the reduction in inventories and inflation in the economy. This situation is considered an inflationary gap—the difference between aggregate demand beyond full employment and aggregate demand at full employment. Aggregate demand is the AD curve and aggregate supply is the AS curve (as shown in the diagram below). While the aggregate demand curve and the aggregate supply curve intersect each other, the full employment equilibrium is attained at Point E. OY is the full employment level of output, and EY is the aggregate demand at full employment level of output. If the aggregate demand increases beyond the full employment level of output from EY to FY, then the economy will have excess demand (FY − EY = FE).
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
State the determinants of aggregate demand.
Explain the concept of 'deficient demand' in macroeconomics.
What is aggregate demand?
Explain how government spending can be helpful in removing deficient demand.
Why does consumption curve not start from the origin?
Name any two components of 'aggregate demand'.
Discuss the situation when aggregate demand is more than aggregate supply at full employment income level.
Explain with reason, whether you agree or disagree with the following statement:
Aggregate supply is influenced only by availability of natural resources.
State whether the following statements are True or False with reason:
Income earned from foreign investment is considered for aggregate demand.
Match the following Group:
| Group A | Group B | ||
| 1) | Aggregate Supply | a) | Expected receipts |
| 2) | Autonomous Investment | b) | Lord J. M. Keynes |
| 3) | Consumption | c) | Government Investment |
| 4) | A.P.C. | d) | ΔC/ΔY |
| 5) | Investment | e) | C/Y |
| f) | Addition to stock of capital | ||
| g) | Destruction of utility | ||
Distinguish between:
Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply
Write Short note on:
Average Propensity to Consume
State with reason whether you agree or disagree with the following statement.
Positive net earnings from foreign transactions add to aggregate demand.
In a closed economy, aggregate demand is the sum of ______.
In case of an under-employment equilibrium, which of the following alternatives is not true?
Identify the correctly matched pair from Column A to Column B:
| Column A | Column B |
| (1) Y = AD | (a) Level of output at full employment |
| (2) Forward Multiplier | (b) Withdrawal of investment decreases income |
| (3) Paradox of Thrift | (c) People save less or same as before |
| (4) Multiplier (k) < 1 | (d) 0 < MPC < 1 |
The equilibrium level of income/output is established when ______
“In an economy ex-ante Aggregate Demand is less than ex-ante Aggregate Supply.”
Explain its impact on the level of output, income and employment.
