Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain price and output determined under monopolistic competition with help of the diagram.
उत्तर
Monopolistic competition refers to a market situation where there are many firms selling differentiated products.
Price and output determination:
Nature of cost and revenue curves:
The monopolistic firm sells large quantities at less price. So, it faces a downward-sloping demand curve. AR curve is fairly elastic. MR curve falls below AR. AC curve will be ‘U’ shaped.
Condition for equilibrium:
MC = MR, MC curve should cut MR from below. If MC is less than MR, the sellers will find it profitable to expand their output.
- Short-run equilibrium:

Profit is maximised when MC = MR. From the diagram.
OM – Equilibrium output OP – Equilibrium price
TR – OMQP TC – OMRS
Profit = OMQP-OMRS
= PQRS
This is super normal profit in the short run.
A monopolistic competitive firm may also incur a loss in the short run.
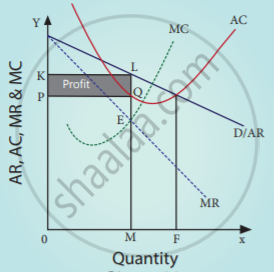
As shown in the diagram, the AR and MR curves are fairly elastic.
At equilibrium output is OM, price is OP
TR – OMQP
TC-OMLK
Total loss = TR-TC
= OMQP – OMLK
= PQLK
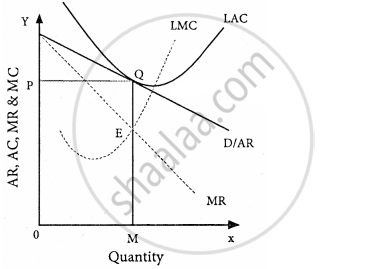
- Long-run equilibrium:
In the long run, the AR curve is more elastic or flatter. Hence, the firms will only earn a normal profit.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Which of the following is a feature of monopolistic competition?
Group equilibrium is analysed in ______.
In monopolistic competition, the essential feature is ______.
Monopolistic competition is a form of ______.
Which of the following involves maximum exploitation of consumers?
Explain any three features of a monopolistic market.
The following diagram represents the demand curve of a firm under ______.
Which of the following market types has a large number of firms that sell similar but slightly different products?
Give two reasons why monopolistic competition is the most realistic form of a market.
Under which market form firm is price taker?
