Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain the electromeric effect.
उत्तर
Electromeric is a temporary effect which operates in unsaturated compounds (containing > C = C <, > C = 0, etc…) in the presence of an attacking reagent.
Let us consider two different compounds.
- compounds containing carbonyl group ( > C = O)
- unsaturated compounds such as alkenes ( > C = C < )
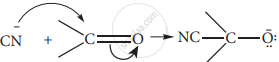
- When a nucleophile approaches the carbonyl compound, the n electrons between C and O is instantaneously shifted to the more electronegative oxygen. This makes the carbon electron-deficient and thus facilitating the formation of a new bond between the incoming nucleophile and the carbonyl carbon atom.
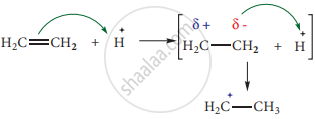
- On the other hand when an electrophile such as H+ approaches an alkene molecule, the π electrons are instantaneously shifted to the electrophile and a new bond is formed between carbon and hydrogen. This makes the other carbon electron-deficient and hence it acquires a positive charge.
- The electrometric effect, is denoted as E effect. Like the inductive effect, the electrometric effect is also classified as + E and – E based on the direction in which the pair of electrons is transferred to form a new bond with the attacking agent.
- When the π electron is transferred towards the attacking reagent, it is called + E (positive electrometric) effect.
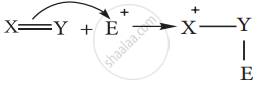
The addition of H+ to alkene as shown above is an example of +E effect.
When the π electron is transferred away from the attacking reagent, it is called, -E (negative electrometric) effect.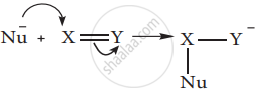
- The attack of CN– on a carbonyl carbon, as shown above, is an example of – E effect.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
For the following reactions
- \[\ce{CH3CH2CH2Br + KOH → CH3 – CH = CH2 + KBr + H2O}\]
- \[\ce{(CH3)3CBr + KOH → (CH3)3COH + KBr}\]
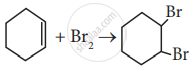
Which of the following statement is correct?
What is the hybridisation state of benzyl carbonium ion?
Homolytic fission of covalent bond leads to the formation of ______.
- I effect is shown by ______.
Which of the following carbocation will be most stable?
Which of the following represent a set of nucleophiles?
Write a short note on hyperconjucation.
What is electrophiles? Give a suitable example.
What is nucleophiles? Give a suitable example.
Show the heterolysis of a covalent bond by using curved arrow notation and complete the following equation. Identify the nucelophile.
\[\ce{CH3 – O – CH3 + HI →}\]
