Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain the experimental determination of the material of the prism using a spectrometer.
उत्तर
- Angle of the prism (A)

Angle of prism
- The prism is placed on the prism table with its refracting edge facing the collimator.
- The slit is illuminated by a sodium light (monochromatic light). The parallel rays coming from the collimator fall on the two faces AB and AC.
- The telescope is rotated to the position T1 until the image of the slit formed by the reflection at the face AB is made to coincide with the vertical cross wire of the telescope.
- The readings of the verniers are noted. The telescope is then rotated to the position T2 where the image of the slit formed by the reflection at the face AC coincides with the vertical cross wire. The readings are again noted.
- The difference between these two readings gives the angle rotated by the telescope, which is twice the angle of the prism. Half of this value gives the angle of the prism A.
- Angle of minimum deviation (D):
- The prism is placed on the prism table so that the light from the collimator falls on a refracting face, and the refracted image is observed through the telescope. The prism table is now rotated so that the angle of deviation decreases.
- A stage comes when the image stops for a moment and if we rotate the prism table further in the same direction, the image is seen to recede and the angle of deviation increases.
- The vertical cross wire of the telescope is made to coincide with the image of the slit where it turns back. This gives the minimum deviation position.
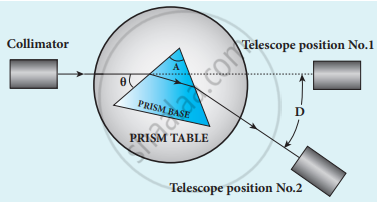
Angle of minimum deviation - The readings of the verniers are noted. Now, the prism is removed, and the telescope is turned to receive the direct ray and the vertical cross wire is made to coincide with the image. The readings of the verniers are noted.
- The difference between the two readings gives the angle of minimum deviation D. The refractive index of the material of the prism n is calculated using the formula,
n = `sin("A+D"/2)/sin("A"/2)`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Answer the following question in detail.
Define and describe the magnifying power of an optical instrument.
What is the near point focusing?
What are the advantages and disadvantages of using a reflecting telescope?
What is the use of collimator in a spectrmeter?
What are the uses of spectrometer?
What is myopia?
What is the remedy of myopia?
What is hypermetropia?
What is the remedy of hypermetropia?
What is presbyopia?
What is astigmatism? What is its remedy?
A compound microscope has a magnification of 30. The focal length of eye piece is 5 cm. Assuming the final image to be at least distance of distinct vision, find the magnification produced by the objective.
There are four convex lenses L1, L2, L3 and L4 of focal length 2, 4, 6 and 8 cm, respectively. Two of these lenses from a telescope of length 10 cm and magnifying power 4. The objective and eye lenses are respectively
The magnifying power of a telescope is high if its objective and eyepiece have respectively ______.
An object viewed from a near point distance of 25 cm, using a microscopic lens with magnification '6', gives an unresolved image. A resolved image is observed at infinite distance with a total magnification double the earlier using an eyepiece along with the given lens and a tube of length 0.6 m, if the focal length of the eyepiece is equal to ______ cm.
Magnification produced by astronomical telescope for normal adjustment is 10 and length of telescope is 1.1 m. The magnification when the image is formed at least distance of distinct vision (D = 25 cm) is ______.
A camera objective has an aperture diameter of d. If the aperture is reduced to diameter d/2, the exposure time under identical conditions of light should be made ______.
