Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain the formation of primary and secondary rainbow.
दीर्घउत्तर
उत्तर
When the sun shines upon falling raindrops, an observer with his back towards the sun sees concentric arcs of spectral colours hanging in the sky. These coloured arcs, which have their common centre on the line joining the sun and the observer, are called 'rainbow'. Usually, two rainbows are seen, one above the other.
The lower one is called the 'primary' rainbow and the higher one is called the 'secondary' rainbow. The primary rainbow is brighter and narrower, having its inner edge violet and the outer edge red. The secondary rainbow, which is comparatively fainter, has reverse order of colours.
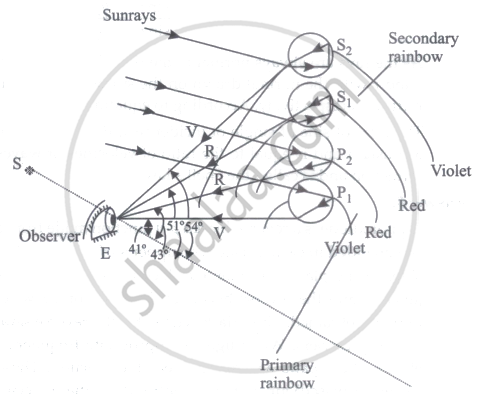
- Formation of Primary Rainbow: Rainbows are formed by the dispersion of sunrays in raindrops. The primary rainbow is formed when sunrays, after suffering one internal reflection in the raindrops, emerge at minimum deviation and enters the observer's eye. In figure, P1 and P2 are two raindrops, Eis the observer's eye and S is the sun. The sun rays fall on the drops parallel to SE. If the rays are deviated (and dispersed) by the drops so as to arrive at the observer, the observer would receive intense light in those directions in which the rays suffer minimum deviation. It can be shown that he would receive red light in a direction making an angle of 43°, and intense violet light in a direction making an angle of 41° with the line SE produced. The drops sending the intense red and violet light to the observer lie on concentric circles which generate cones of semivertical angles of 43° and 41° respectively with common vertex at E. Thus, the observer sees concentric coloured arcs of which the innermost is violet and the outermost is red. The intermediate colours lie in between. This is the primary rainbow.
- Formation of Secondary Rainbow: The secondary fainter rainbow is formed by the sunrays undergoing two internal reflections in the raindrops and emerging at minimum deviation, as occurring in drops S1 and S2 in the figure. The semivertical angles for this bow are 51° for the red rays to 54° for the violet rays. As such, the order of colours is reverse of that in the primary rainbow.
shaalaa.com
क्या इस प्रश्न या उत्तर में कोई त्रुटि है?
