Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain the rules for obtaining images formed by a convex lens with the help of ray diagram.
उत्तर
- Rule 1: When a ray of light strikes the convex or concave lens obliquely at its optical centre, it continues to follow its path without any deviation.

Rays passing through the optical centre - Rule-2: When rays parallel to the principal axis strikes a convex or concave lens, the refracted rays are converged to (convex lens) or appear to diverge from (concave lens) the principal focus
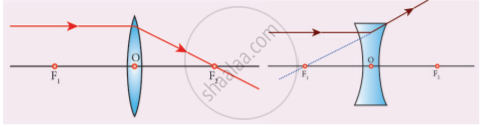
Rays passing parallel to the optic axis - Rule-3: When a ray passing through (convex lens) or directed towards (concave lens) the principal focus strikes a convex or concave lens, the refracted ray will be parallel to the principal axis
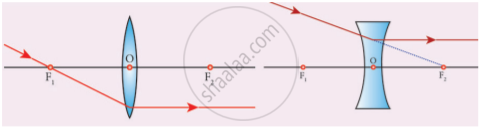
Rays passing through or directed towards the principal focus
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A lens forms an upright and diminished image of an object when the object is placed at its focal point. Name the lens and draw a ray diagram to show the image formation.
A converging lens forms the image of an object placed in front of it, beyond 2F2 of the lens. State three characteristics of the image.
An object is placed at a distance of more than 40 cm from a convex lens of focal length 20 cm. The image formed is real, inverted and ______.
An object is placed at a distance 5 cm from a convex lens of focal length 10 cm. The image formed is virtual, upright and _____.
For the object placed between the optical centre and focus of a convex lens, the image is ______.
Where should an object be placed so that a real and inverted image of the same size is obtained by a convex lens?
A small bulb is placed at the principal focus of a convex lens. When the bulb is switched on, the lens will produce
Which of the following lens would you prefer to use while reading small letters found in a dictionary?
Draw ray diagrams showing the image formation by a convex lens when an object is placed
- between optical centre and focus of the lens
- between focus and twice the focal length of the lens
- at twice the focal length of the lens
- at infinity
- at the focus of the lens
A lens forms an upright and magnified image of an object. Draw a labelled ray diagram to show the image formation.
