Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain the structure of a typical antibody molecule.
उत्तर
Structure of an Antibody (Gk. anri-against, body-body) Antibody is a glycoprotein, called immunoglobulin, which have a specific amino acid sequences by which they can interact with specific antigens. Antibodies form 20% of the plasma proteins. Each antibody has a combination of at least 2 light (L) and 2 heavy (H) polypeptide chains. The heavy chains have a larger number of amino acids while the lighter chain has a smaller number of them. Usually, the polypeptides form a Y-shaped configuration. The stem of Y is exclusively formed by heavy chains. In the arms of Y, both light and heavy chains occur parallel to each other except for antigen-binding sites. Attachments and bendings occur by means of disulphide bonds (—S—S—). In certain immunoglobulins the number of chain pairs can be JO. An antibody has a variable portion in the arms. It is called V-region or antigen-binding fragment, Fab. The remainder of the antibody is called constant portion or crystalline fragment, Fc.
Most of the antibodies function as monomers. A few such as IgA, IgM can occur both as monomers and polymers.
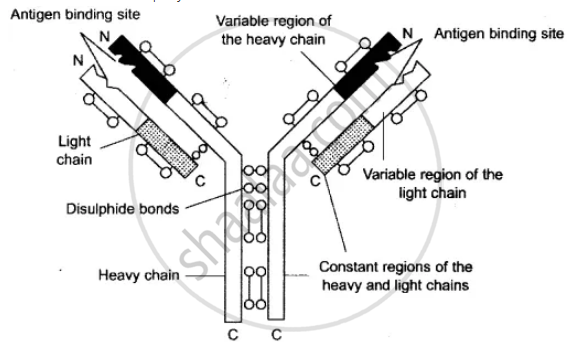
A Typical antibody molecule
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
In which way has the study of biology helped us to control infectious diseases?
Name the scientists who Invented the CT scan
Which part of the brain extends to form spinal cord?
On 11th March 2020, the World Health Organisation characterized the COVID-19 outbreak as ______.
When an apparently healthy person is diagnosed as unhealthy by a psychiatrist, the reason could be that ______.
Given below are some of the things that are necessary for achieving good health. Identify the wrong one.
The term ' health' is defined in many ways. The most accurate definition of health would be
Diseases are broadly grouped into infectious and non-infectious diseases. In the list given below, identify the infectious diseases.
- Cancer
- Influenza
- Allergy
- Small pox
What is secondary metabolism?
A patient was advised to have a kidney transplant. To suppress the immune reaction, the doctor would administer him ______.
