Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain the terms Inductive and Electromeric effects.
उत्तर
Inductive effect:
The permanent displacement of sigma (σ) electrons along a saturated chain, whenever an electron-withdrawing or electron-donating group is present, is called the inductive effect.
Inductive effect could be + I effect or – I effect. When an atom or group attracts electrons towards itself more strongly than hydrogen, it is said to possess – I effect. For example,

When an atom or group attracts electrons towards itself less strongly than hydrogen, it is said to possess + I effect. For example,
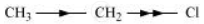
Electrometric effect:
It involves the complete transfer of the shared pair of π electrons to either of the two atoms linked by multiple bonds in the presence of an attacking agent. For example,
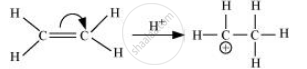
Electrometric effect could be + E effect or – E effect.
- + E effect: When the electrons are transferred towards the attacking reagent.
- – E effect: When the electrons are transferred away from the attacking reagent.
