Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain why alkyl groups act as electron donors when attached to a π system
उत्तर
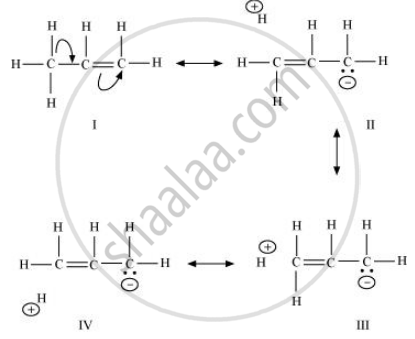
When an alkyl group is attached to a π system, it acts as an electron-donor group by the process of hyperconjugation. To understand this concept better, let us take the example of propene.
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{H}\phantom{....}\ce{H}\phantom{....}\ce{H}\\
\backslash\phantom{.....}|\phantom{.....}|\\
\ce{H - C - C = C - H}\\
/\phantom{...........}\\
\ce{H}\phantom{.............}\end{array}\]
In hyperconjugation, the sigma electrons of the C–H bond of an alkyl group are delocalised. This group is directly attached to an atom of an unsaturated system. The delocalisation occurs because of a partial overlap of a sp3 –s sigma bond orbital with an empty p orbital of the π bond of an adjacent carbon atom.
The process of hyperconjugation in propene is shown as follows:
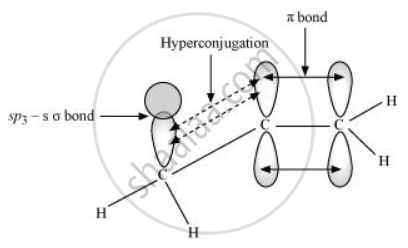
This type of overlap leads to a delocalisation (also known as no-bond resonance) of the π electrons, making the molecule more stable.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Hyperconjugation involves delocalisation of:
(i) Electrons of carbon-hydrogen σ bond of an alkyl group directly attached to an atom of unsaturated system.
(ii) Electrons of carbon-hydrogen σ bond of alkyl group directly attached to the positively charged carbon atom.
(iii) π-electrons of carbon-carbon bond.
(iv) Lone pair of electrons.
The activating nature of \[\ce{- CH3}\] group linked to benzene ring can be explained with the help of ______.
