Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain why the tax multiplier is smaller in absolute value than the government expenditure multiplier.
उत्तर
The tax multiplier is smaller in absolute value than the government expenditure multiplier, as the government expenditure affects the total expenditure and taxes through the multiplier. Tax multiplier also influences disposable income that affects the overall consumption level.
The reason is explained through the following example.
Let’s assume MPC be to 0.80.
Then, the government expenditure multiplier `=1/(1-c)`
`=1/(1-0.80)`
`=1/0.20=5`
Tax multiplier `=(-c)/(1-c)=(-0.80)/(1-0.80)`
`=(-0.80)/0.20=-4`
This shows that government expenditure multiplier is more than tax multiplier.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Distinguish between revenue deficit and fiscal deficit.
Explain 'Revenue Deficit in a Government budget? What does it indicate?
State the relation between marginal revenue and average revenue.
Give the relationship between the revenue deficit and the fiscal deficit.
Consider an economy described by the following functions:- C = 20 + 0.80Y, I = 30, G = 50, TR = 100 (a) Find the equilibrium level of income and the autonomous expenditure multiplier in the model. (b) If government expenditure increases by 30, what is the impact on equilibrium income? (c) If a lump-sum tax of 30 is added to pay for the increase in government purchases, how will equilibrium income change?
Consider an economy described by the following functions:- C = 20 + 0.80Y, I = 30, G = 50, TR = 100, calculate the effect on output of a 10 per cent increase in transfers, and a 10 per cent increase in lump-sum taxes. Compare the effects of the two.
Explain the relation between government deficit and government debt.
Discuss the issue of deficit reduction.
Answer the following question.
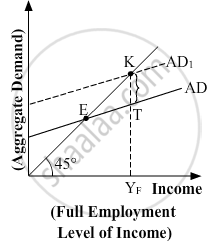
In the given figure, what does the gap 'KT' represent? State any two fiscal measures to correct the situation.
Suppose you are a member of the "Advisory Committee to the Finance Minister of India". The Finance Minister is concerned about the rising Revenue Deficit in the budget.
Suggest anyone measure to control the rising Revenue Deficit of the government.
Which of the following statement is true?
| S. No. | Content | Rs (in crores) |
| 1. | Revenue Expenditure | 100 |
| 2. | Capital Receipts | 40 |
| 3. | Net Borrowings | 38 |
| 4. | Net Interest Payments | 27 |
| 5. | Tax Revenue | 50 |
| 6. | Non-tax Revenue | 15 |
Which of the following is MOST LIKELY to be the main contributor to the fiscal deficit in this case?
Assertion (A): Fiscal deficit is measured in terms of borrowings.
Reason (R): External borrowings increases the Fiscal deficit.
Read the following statements carefully and choose the correct alternatives given below:
Statement 1: Fiscal Deficit = Total Budget Expenditure - Total Budget Receipts (Net of borrowing)
Statement 2: Primary Deficit = Fiscal Deficit + Interest Payments.
A fiscal deficit is equal to borrowings. It is ______
Which of the following statements are correct
Statement 1: Fiscal deficits are not necessarily inflationary; though, they are generally regarded as inflationary.
Statement 2: When the government expenditure increases and tax reduces, there is a government deficit and there will be a corresponding increase in the aggregate demand.
Which of the following transactions are correct about ORT?
Fiscal Deficit equals:
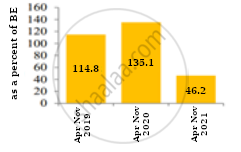
Compare the trends depicted in the figures given below:
| Figure 1: Trends in Fiscal deficit and Primary deficit |
Figure 2: Fiscal deficit as a percent of Budget estimate |
 |
 |
A large amount of fiscal deficit proves to be counter productive. Give any two reasons in support of this statement.
