Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
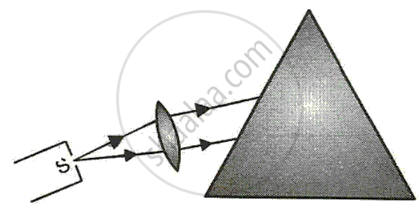
Fig shows part of the arrangement for obtaining pure spectrum.
(a) Complete thediagram and show how to obtain a pure spectrum.
(b) What are the conditions necessary for obtaining a pure spectrum?
उत्तर
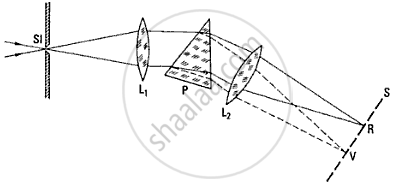
(a)
(b)
A pure spectrum is that spectrum in which the different colours are distinctly seen without any overlapping. Following conditions must be satisfied to get a pure spectrum.
- The slit (placed in front of the source) must be narrow as possible. A wide slit is equivalent to a large number of narrow slits placed side by side. Each narrow slit will give its own spectrum. So, there will be overlapping of different spectra.
- The ray of light in the incident beam must be parallel to each other. This is achieved by using a convex lens. A convex lens should be so placed that the slit is at its focus.The convex lens used in this way is called collimating lens while the beam emerging out of this lens is called collimated beam.
If the incident beam is parralel, Then in the refracted beam, all the rays of the same colour will be parallel and will be focussed seperately. - The prism must be placed in the minimum deviation position. When the prism is placed in the position of minimum deviation, all the rays are deviated by equal amounts. This ensures freedom from overlappng.
- On emergence from the prism, all rays of one colour should form a parallel beam of their own. if a convex lens is suitably placed in the path of these rays, then each parallel beam will come to its own focus. In this way, a pure spectrum will be obtained.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Why is the colour red used as a sign of danger?
Which colour of white light travels fastest in glass?
In following diagram shows a thin beam of white light from a source S striking on one face of a prism.
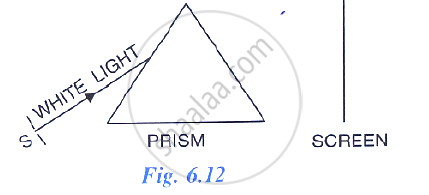
A slit is placed in between the prism and the screen to pass only the light of green colour. What will you then observe on the screen?
In following diagram shows a thin beam of white light from a source S striking on one face of a prism.
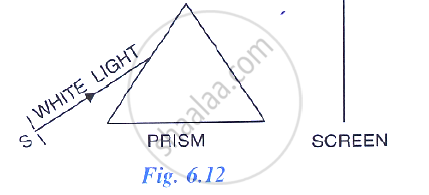
What conclusion do you draw from the observation in part (b) above?
If a monochromatic beam of light undergoes minimum deviation through an equiangular prism, how does the beam pass through the prism, with respect to its base?
Light of different colours is deviated through different angles, by a prism. Explain the reason.
Give a reason, why the violet colour of white light deviated most and red colour of white light deviated least.
Name the radiation of a wavelength longer than 8 × 10−7 m.
A prism causes dispersion of white light while a rectangular glass block does not. Explain.
Which colour of white light travels slowest, in glass?
