Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Figure shows some of the equipotential surfaces of the magnetic scalar potential. Find the magnetic field B at a point in the region.
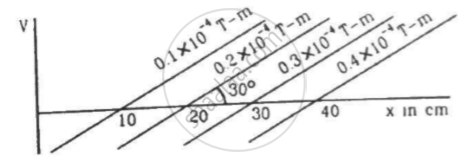
उत्तर
Given :
Perpendicular distance, `dx = 10 sin 30^circ "cm" = 0.05 "m"` ,
Change in the potential, dV = `0.1 xx 10^-4 "T-m"`
We know that the relation between the potential and the field is given by
`B = -(dV)/(dx)`
⇒ `B = -(0.1 xx 10^-4 "T-m")/(5 xx 10^-2 "m")`
⇒ `B = -2 xx 10^-4 "T"`
B is perpendicular to the equipotential surface. Here, it is at angle of 120° with the positive x-axis.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
State any two advantages of electromagnets over permanent magnets.
Write two characteristics of a material used for making permanent magnets ?
Magnetic scalar potential is defined as `U(vec r_2) - U(vec r_1) = - ∫_vec(r_1)^vec(r_2)` `vec (B) . dvec(l)`
Apply this equation to a closed curve enclosing a long straight wire. The RHS of the above equation is then `-u_0 i` by Ampere's law. We see that `U(vec(r_2)) ≠ U(vec(r_1))` even when `vec r_2 =vec r_1` .Can we have a magnetic scalar potential in this case?
A dip circle is taken to geomagnetic equator. The needle is allowed to move in a vertical plane perpendicular to the magnetic meridian. The needle will stay ______.
A very long bar magnet is placed with its north pole coinciding with the centre of a circular loop carrying as electric current i. The magnetic field due to the magnet at a point on the periphery of the wire is B. The radius of the loop is a. The force on the wire is
A uniform magnetic field of `0.20 xx 10^-3 "T"` exists in the space. Find the change in the magnetic scalar potential as one moves through 50 cm along the field.
Why is it not possible to make permanent magnets from paramagnetic materials?
The magnetic moment of the assumed dipole at the earth's centre is 8.0 × 1022 A m2. Calculate the magnetic field B at the geomagnetic poles of the earth. Radius of the earth is 6400 km.
A magnetic needle is free to rotate in a vertical plane which makes an angle of 60° with the magnetic meridian. If the needle stays in a direction making an angle of `tan^-1(2sqrt(3))` with the horizontal, what would be the dip at that place?
The needle of a dip circle shows an apparent dip of 45° in a particular position and 53° when the circle is rotated through 90°. Find the true dip.
Which property of soft iron makes it useful for preparing electromagnet?
Answer in brief.
Explain one application of electromagnet.
A thin diamagnetic rod is placed vertically between the poles of an electromagnet. When the current in the electromagnet is switched on, then the diamagnetic rod is pushed up, out of the horizontal magnetic field. Hence the rod gains gravitational potential energy. The work required to do this comes from ______.
In a permanent magnet at room temperature ______.
The relation b/w magnetic susceptibility xm and relativ~ permeability µr is
Which magnetic properties are desirable for making a permanent magnet?
