Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The carrier wave is given by
C(t) = 2sin(8πt) volt.
The modulating signal is a square wave as shown. Find modulation index.
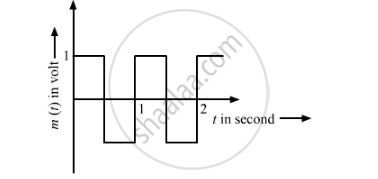
उत्तर
Modulation index (μ) is the ratio of the amplitude of the modulating signal to the amplitude of the carrier wave.
The generalised equation of a carrier wave is given below:
c(t) =Acsinωct
The generalised equation of a modulating wave is given below:
cm(t)=Acsinωct+μAcsinωmtsinωct
Here, μ is defined as `A_m/A_c`
On comparing this with the equations of carrier wave and modulating wave, we get:
Amplitude of modulating signal, Am=1 V
Amplitude of carrier wave, Ac=2 V
`:.mu=A_m/A_c=1/2=0.5`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Draw a sketch of a sinusoidal carrier wave along with a modulating signal and show how these are superimposed to obtain the resultant amplitude modulated wave
How are side bands produced?
A carrier wave of peak voltage 15 V is used to transmit a message signal. Find the peak voltage of the modulating signal in order to have a modulation index of 60%
In a communication system, what is meant by modulation?
The carrier wave of a signal is given by C(t) = 3 sin (8πt) volt. The modulating signal is a square wave as shown. Find its modulation index.

In the given block diagram of a receiver, identify the boxes labeled as X and Y and write their functions.
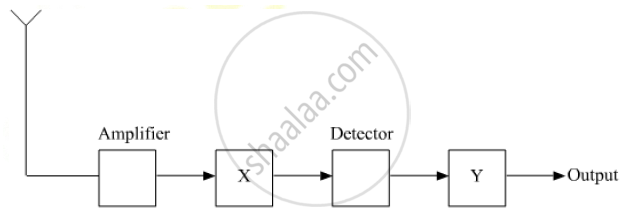
Answer the following question.
Why a signal transmitted from a TV tower cannot be received beyond a certain distance? Write the expression for the optimum separation between the receiving and the transmitting antenna.
A 100 m long antenna is mounted on a 500 m tall building. The complex can become a transmission tower for waves with λ.
A speech signal of 3 kHz is used to modulate a carrier signal of frequency 1 MHz, using amplitude modulation. The frequencies of the sidebands will be ______.
A carrier wave Vc(t) = 160 sin(2π × 106t) volts is made to vary between Vmax = 200 V and Vmin = 120 V by a message signal Vm(t) = Am sin(2π × 103t) volts. The peak voltage Am of the modulating signal is ______.
