Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
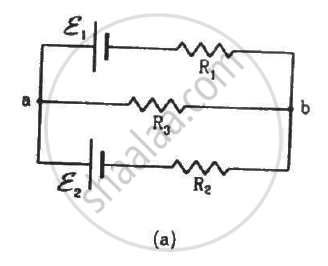
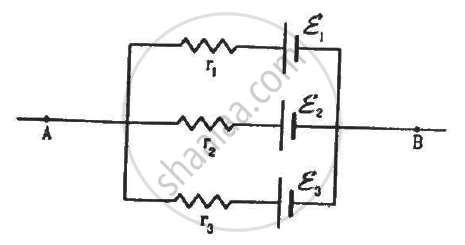
Find the potential difference Va – Vb in the circuits shown in the figure.
उत्तर

Applying KVL in loop 1, we get:-
\[i_1 R_2 - E_2 + \left( i_1 + i_2 \right) R_3 = 0\]
\[( R_2 + R_3 ) i_1 + R_3 i_2 = E_2 ...........(1)\]
Applying KVL in loop 2, we get:-
\[i_2 R_1 - E_1 + \left( i_1 + i_2 \right) R_3 = 0\]
\[\left( R_1 + R_3 \right) i_2 + R_3 i_1 = E_1 .............(2)\]
Multiplying equation (1) by (R1+R3) and (2) by R3 and then subtracting (2) from (1), we get:-
\[i_1 = \frac{E_2 \left( R_1 + R_3 \right) - E_1 R_3}{\left( R_1 R_2 + R_2 R_3 + R_3 R_1 \right)}\]
Similarly, multiplying equation (1) by R3 and (2) by (R1+R3), and then subtracting (2) from (1), we get:-
\[i_2 = \frac{E_1 \left( R_2 + R_3 \right) - E_2 R_3}{\left( R_1 R_2 + R_2 R_3 + R_3 R_1 \right)}\]
From the figure,
\[V_a - V_b = \left( i_1 + i_2 \right) R_3 \]
\[ \Rightarrow V_a - V_b = \left[ \frac{E_1 R_2 + E_2 R_1}{\left( R_1 R_2 + R_2 R_3 + R_3 R_1 \right)} \right] R_3 \]
\[ \Rightarrow V_a - V_b = \frac{\frac{E_1}{R_1} + \frac{E_2}{R_2}}{\frac{1}{R_1} + \frac{1}{R_2} + \frac{1}{R_3}}\]
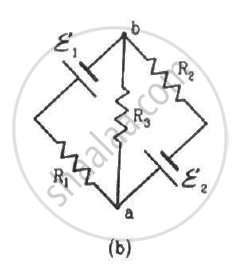
(b) The circuit in figure b can be redrawn as shown below:-
We can see that it is similar to the circuit in figure a and, hence, the answer obtained will be same.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
In the following potentiometer circuit, AB is a uniform wire of length 1 m and resistance 10 Ω. Calculate the potential gradient along the wire and balance length AO (= l).
When 5 V potential difference is applied across a wire of length 0.1 m, the drift speed of electrons is 2.5 x 10-4 m/s. If the electron density in the wire is 8 x 1028 m-3, calculate the resistivity of the material of the wire.
Describe the working principle of a solar cell. Mention three basic processes involved in the generation of emf.
Why are Si and GaAs preferred materials for solar cells?
Why is potentiometer preferred over a voltmeter for comparison of emf. of cells?
Identify the correct options.
(a) An ammeter should have small resistance.
(b) An ammeter should have large resistance.
(c) A voltmeter should have small resistance.
(d) A voltmeter should have large resistance.
The current in a conductor and the potential difference across its ends are measured by an ammeter and a voltmeter. The meters draw negligible currents. The ammeter is accurate but the voltmeter has a zero error (that is, it does not read zero when no potential difference is applied). Calculate the zero error if the readings for two different conditions are 1.75 A, 14.4 V and 2.75 A, 22.4 V.
The potential difference between the terminals of a battery of emf 6.0 V and internal resistance 1 Ω drops to 5.8 V when connected across an external resistor. Find the resistance of the external resistor.
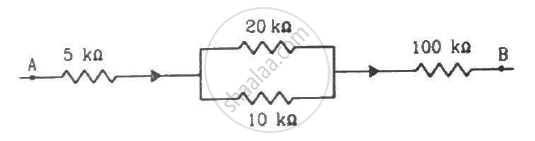
The following figure shows a part of a circuit. If a current of 12 mA exists in the 5 kΩ resistor, find the currents in the other three resistors. What is the potential difference between the points A and B?
In the circuit shown in the figure, ε1 = 3 V, ε2 = 2 V, εa = 1 V and r1 = r2 = r3 = 1Ω. Find the potential difference between the points A and B and the current through each branch.
A voltmeter consists of a 25 Ω coil connected in series with a 575 Ω resistor. The coil takes 10 mA for full-scale deflection. What maximum potential difference can be measured by this voltmeter?
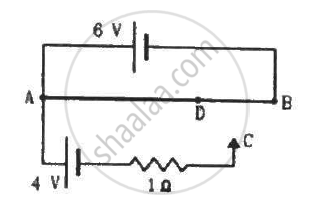
A 6-volt battery of negligible internal resistance is connected across a uniform wire AB of length 100 cm. The positive terminal of another battery of emf 4 V and internal resistance 1 Ω is joined to the point A, as shown in the figure. Take the potential at B to be zero. (a) What are the potentials at the points A and C? (b) At which point D of the wire AB, the potential is equal to the potential at C? (c) If the points C and D are connected by a wire, what will be the current through it? (d) If the 4 V battery is replaced by a 7.5 V battery, what would be the answers of parts (a) and (b)?
A copper strip AB and an iron strip AC are joined at A. The junction A is maintained at 0°C and the free ends B and C are maintained at 100°C. There is a potential difference between _______________ .
(a) the two ends of the copper strip
(b) the copper end and the iron end at the junction
(c) the two ends of the iron strip
(d) the free ends B and C
The potential difference across the terminals of a battery of emf 12 V and internal resistance 2 Ω drops to 10 V when it is connected to a silver voltameter. Find the silver deposited at the cathode in half an hour. Atomic weight of silver is 107.9 g mol−1.
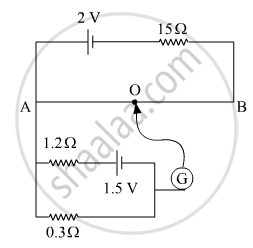
In the circuit in figure the potential difference across P and Q will be nearest to