Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Give one example of An aquatic plant used in the laboratory to demonstrate O2 liberation during photosynthesis
उत्तर
An aquatic plant used in the laboratory to demonstrate the liberation of oxygen during photosynthesis – Hydrilla
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Formalin, Iodine, DDT, Lime
Expand the following biological abbreviations: ATP
Define the following:
Plant pigments
Fill in the blank:
CO2 enters the leaf through ______.
The diagram alongside represents an experiment conducted to prove the importance of a factor in photosynthesis.
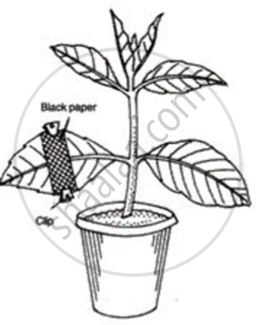
Study the same and then answer the questions that follow:
(i) Name the factor being studied in his experiment.
(ii) Why was the plant kept in a dark room before conducting the experiment?
(iii}Why was the experimental leaf then kept in
1. boiling water 2. methylated spirit?
(iv) Name the solution used to test for the presence of starch in the leaf.
(v) What will we observe in the experimental leaf at the end of the starch test?
(vi) Give a balanced chemical equation to represent the process of photosynthesis.
A plant is kept in a dark cupboard for 48 hours before conducting any experiment on photosynthesis in order to
What are the basic requirements of photosynthesis?
What is the importance of photosynthesis in the life of the following:
Green plants
Photosynthesis is considered as a process supporting all life on earth.
Give technical term:
In photosynthesis radiant energy is converted into which from?
Mention, if the following statement is True or False. If false rewrite the wrong statement in its correct form:
A variegated leaf (one that has green as well as white patches) will only photosynthesize in the green areas.
Choose the Correct Answer:
NADP is expanded as
Column ‘II’ is a list of items related to ideas in Column ‘I’. Match the term in Column ‘II’ with the suitable idea given in Column ‘I’.
| Column I | Column II | ||
| (i) | Grana | (a) | Decomposers |
| (ii) | Autotrophs | (b) | Light reaction |
| (iii) | By-products of photosynthesis | (c) | Animals |
| (iv) | Photolysis | (d) | Oxygen |
| (v) | Bacteria and fungi | (e) | Stimulated by light |
| (vi) | Chloroplast | (f) | Power |
| (vii) | Oxygen and water | (g) | Raw material |
| (viii) | Sunlight | (h) | Machinery |
| (ix) | CO2 and water | (i) | End products |
| (x) | Glucose (sugar) | (j) | Workrooms |
| (xi) | Cells in the leaf | (k) | By-products. |
During photosynthesis, ________ is produced and stored in the leaf.
______ is positively hydrotropic as well as positively geotropic.
Higher Order Thinking Skill.
Imagine that student A studied the importance of certain factors in photosynthesis. He took a potted plant and kept it in dark for 24 hours. In the early hours of the next morning, he covered one of the leaves with dark paper in the centre only. Then he placed the plant in sunlight for a few hours and tested the leaf which was covered with black paper for starch.
- What aspect of photosynthesis was being investigated?
- Why was the plant kept in the dark before the experiment?
- How will you prove that starch is present in the leaves?
- Name the raw materials needed for photosynthesis.
Where do the light-dependent reaction and the Calvin cycle occur in the chloroplast?
Give an example for micronutrients.
Mention four factors required for photosynthesis?
