Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Give scientific reason:
We cannot clearly see an object kept at a distance less than 25 cm from the eye.
उत्तर
- The muscles attached to the eye lens (ciliary muscles) help in fine adjustments of the focal length of the lens.
- The capacity of these muscles to contract or relax to adjust the focal length (i.e., power of accommodation) has a limit.
- The minimum distance of an object from a normal eye for which the eye lens can decrease its focal length to the least possible value, is 25 cm.
Hence, we cannot clearly see an object kept at a distance less than 25 cm from the eye.
संबंधित प्रश्न
Write the function of retina in human eye.
Write the function of the following part of the human eye: Cornea
Explain the following:
Mechanism of generation of light-induced impulse in the retina.
The optical prescription for a pair of spectacles is :
Right eye : −3.50 D
Left eye : −4.00 D
Which is the weaker eye?
Name the part of the eye:
on which the image is formed.
What is the name of:
the curved, transparent front surface of the eye?
Define the term "power of accommodation" of human eye.
The eyes of a person are focused (i) on a nearby object, and (ii) on a distant object, turn by turn. In which case:
the focal length of eye-lens will be the maximum?
Ciliary muscles of human eye can contract or relax. How does it help in the normal functioning of the eye?
There are two types of light-sensitive cells in the human eye:
Where are they found?
Name the cells on the retina of an eye which are sensitive to (i) bright light (ii) dim light (iii) sensation of colour.
How does the eye adjust itself to deal with light of varying intensity?
Explain the functions of the following parts of the eye:
(i) cornea
(ii) iris
(iii) pupil
(iv) ciliary muscles
(v) eye-lens
How does the eye change in order to focus on near or distant objects?
(a) The lens moves in or out
(b) The retina moves in or out
(c) The lens becomes thicker or thinner
(d) The pupil gets larger or smaller
Which of the following changes occur when you walk out of bright sunshine into a poorly lit room?
(a) the pupil becomes larger
(b) the lens becomes thicker
(c) the ciliary muscle relaxes
(d) the pupil becomes smaller
What is presbyopia? Write two causes of this defect. Name the type of lens which can be used to correct presbyopia.
Five persons A, B, C, D and E have diabetes, leukaemia, asthma, meningitis and hepatitis, respectively.
Which of these persons can donate eyes?
The animal which does not have eyes that look sideways is:
(a) Horse
(b) Chicken
(c) Lion
(d) Fish
Given below is certain structure. Write against them its functional acivity.
retina and ……………………….
Mention the characteristics of the image that falls on the retina of the eye.
With reference to the functioning of the eye, answer the question that follow:
Name the two structure in the eye responsible for bringing about the change in the shape of the lens.
Give scientific reason:
One can sense colours only in bright light.
Define the following:
Yellow spot
State the Function:
Choroid coat in the eye
State the Function:
Ear drum
For a normal human eye the near point is at _______.
Write the name.
The fleshy screen behind cornea.
For a healthy human eye, the distant point is infinite distance.
At noon the sun appears white as
Given below is a diagram depicting a defect of the human eye. Answer the questions that follow:
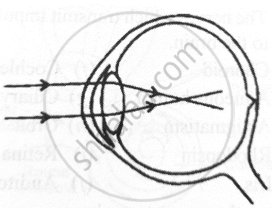
- Give the scientific term for the defect.
- Mention one possible reason for the defect.
- What type of lens can be used to correct the defect?
In the figure of the human eye, the cornea is represented by the letter
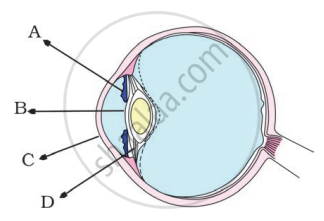
Write in proper sequence the names of all the parts of the human eye through which the light rays coming from an object pass before they form an image on the retina.
Name the following:
Place of no vision in the retina of the eye.
Name the following:
Kind of retinal cells sensitive to dim light.
Name the following:
The layer of the wall of the eye-ball that corresponds to the black lining of the box of a camera
Name the following:
Two pigments of the sensory cells.
Differentiate between members of the following pair with reference to what is asked in the bracket.
Aqueous humour and vitreous humour (location).
