Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Give the biochemical events occurring in the root nodule of a pulse plant. What is the end product? What is its fate?
उत्तर
Nodule Formation:
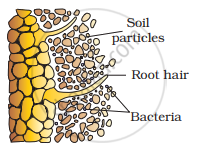
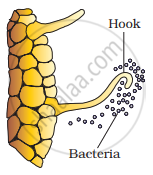
- Rhizobium bacteria contact a susceptible root hair and begin to divide near it.
- After successful infection, the root hair curls.
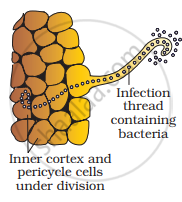
- The infected thread of the root carries the bacteria to the inner cortex. The bacteria get modified into rod-shaped bacteroids. This causes the inner cortical and pericycle cells to divide.
- Division and growth of cortical and pericycle cells result in nodule formation.
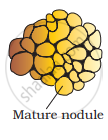
- A mature nodule is complete with vascular tissues, which are continuous with the vascular tissues of the root.
Importance of Leghaemoglobin: Leghaemoglobin works as an oxygen scavenger and thus creates anaerobic conditions in the root nodule of a legume. Nitrogenase is highly sensitive to oxygen and needs an anaerobic condition to maintain its existence.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
What are the conditions necessary for fixation of atmospheric nitrogen by Rhizobium. What is their role in N2 -fixation?
Plants absorb nitrogen as ______.
In Glycine max, the product of biological nitrogen fixation is transported from the root nodules to other parts as ______.
In some plants, like soyabean, fixed nitrogen is exported into the transpiration stream as :
Reaction carried out by N2 fixing microbes include
- \[\ce{2NH3 + 3O2 -> 2NO^{-}2 + 2H^{+} + 2H2O (i)}\]
- \[\ce{2NO^{-}2 + O2 -> 2NO^{-}3 (ii)}\]
Which of the following statements about these equations is not true
With regard to the Biological Nitrogen Fixation by Rhizobium in association with soybean, which one of the following statement/ statements does not hold true.
Nitrogen fixation is shown by prokaryotes and not by eukaryotes. Comment.
What is the function of leghaemoglobin in the root nodule of a legume?
Rice fields produce an important greenhouse gas. Name it.
Complete the equation for reductive amination
\[\ce{->[?] + NH^{+}4 + NADPH ->[][?] glutamate + NADP + H2O}\]
