Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
उत्तर
Two properties of ultraviolet radiation different from the visible light:
1. Ultraviolet radiation can pass through quartz, but they are absorbed by glass.
2. They are usually scattered by the dust particles present in the atmosphere.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Which radiation is used for satellite communication?
What is the range of the wavelength of the following electromagnetic waves?
(a) Gamma rays.
The wavelength of X-rays is 0.01 Å. Calculate its frequency. State the assumption made, if any.
Characteristic X-rays may be used to identify the element from which they are being emitted. Can continuous X-rays be used for this purpose?
Two waves A and B have wavelength 0.01 Å and 9000 Å respectively.
Name the two waves. compare the speeds of these waves when they travel in vacuum.
| Gamma rays | D | C | Visible light | B | A |
The above table shows different parts of the electromagnetic spectrum.
(a) Identify the parts of the spectrum marked as A, B, C and D.
(b) Which of the radiations A or B has the higher frequency?
(c) State two properties which are common to all parts of the electromagnetic spectrum.
(d) Name one source of each of the radiation of electromagnetic spectrum.
(e) Name one detector for each of the radiation.
(f) Name one use of each of the radiation.
To which regions of the electromagnetic spectrum do the following wavelengths belong:
(a) 250 nm
(b) 1500 nm
If the Earth did not have atmosphere, would its average surface temperature be higher or lower than what it is now? Explain.
Electromagnetic waves with wavelength
- λ1 is suitable for radar systems used in aircraft navigation.
- λ2 is used to kill germs in water purifiers.
- λ3 is used to improve visibility in runways during fog and mist conditions.
Identify and name the part of the electromagnetic spectrum to which these radiations belong. Also arrange these wavelengths in ascending order of their magnitude.
In an atom X, electrons absorb the energy from an external source. This energy “excites” the electrons from a lower-energy level to a higher-energy level around the nucleus of the atom. When electrons return to the ground state, they emit photons.
The figure below is the energy level diagram of atom X with three energy levels, E1 = 0.00eV, E2 = 1.78eV and E3 = 2.95eV. The ground state is considered 0 eV for reference. The transition of electrons takes place between levels E1 and E2.
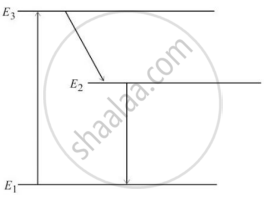
- What wavelength of radiation is needed to excite the atom to energy level E2 from E1?
- Suppose the external source has a power of 100 W. What would be the rate of photon emission?
