Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
(a) Given below is a pyramid of biomass in an ecosystem where each bar represents the standing crop available in the trophic level. With the help of an example explain the conditions where this kind of pyramid is possible in nature.
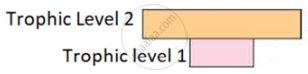
(b) Will the pyramid of energy be also of the same shape in this situation? Give a reason for your response.
उत्तर
(a) Invertebrate biomass pyramids can be observed in aquatic environments where a tiny standing phytoplankton crop supports a huge standing zooplankton/fish crop or in terrestrial ecosystems where a lot of insects are eating on a tree's leaves.
(b) No, the Pyramid of Energy is always upright and cannot be inverted because some energy is constantly lost as heat at each trophic level as it moves from one to the next.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Why the pyramid of energy is always upright? Explain.
In a food chain, the herbivores are represented by
(A) producers
(B) primary consumers
(C) secondary consumers
(D) decomposers
Which organisms constitute the last trophic level?
Explain with the help of labelled diagrams, the difference between an upright pyramid of biomass and an inverted pyramid of biomass.
Secondary consumers are __________.
Give an example of an ecosystem that shows an inverted pyramid of biomass.
Which one of the following is not used for construction of ecological pyramids?
In an aquatic ecosystem, a mollusc typically belongs to-
Draw a diagram of pyramid of energy.
The biomass of a standing crop of phytoplankton is 4 kg/m2, which supports a large standing crop of zooplankton having a biomass of 11 kg/m2. This is consumed by small fishes having a biomass of 25 kg/m2, which are then consumed by large fishes with a biomass of 37 kg/m2.
Draw an ecological pyramid indicating the biomass at each stage and also name the trophic levels. Mention whether it is an upright or inverted pyramid.
