Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
How do you explain the absence of aldehyde group in the pentaacetate of D-glucose?
उत्तर १
D-glucose reacts with hydroxylamine (NH2OH) to form an oxime because of the presence of aldehydic (−CHO) group or carbonyl carbon. This happens as the cyclic structure of glucose forms an open chain structure in an aqueous medium, which then reacts with NH2OH to give an oxime.
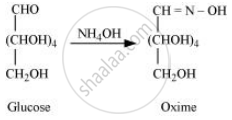
But pentaacetate of D-glucose does not react with NH2OH. This is because pentaacetate does not form an open chain structure.

उत्तर २
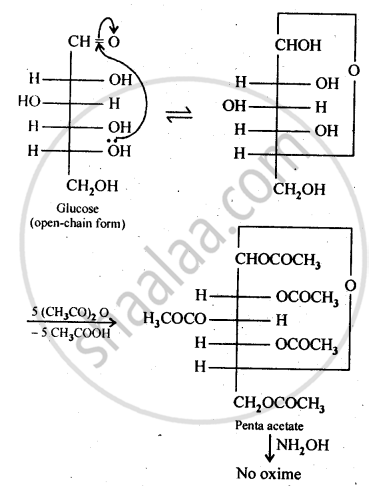
The cyclic hemiacetal form of glucose contains an -OH group at C-l which gets hydrolysed in aqueous solution to produce open chain aldehydic form which then reacts with NH2OH -to form corresponding oxime. Thus, glucose contains an aldehydic group. However, when glucose is reacted with acetic anhydride, the -OH group at C-l along with the other -OH groups at C-2, C-3, C-4 and C-6 form a pentaacetate.
Since the penta acetate of1 glucose does not contain a free -OH group at C-l, it cannot get hydrolysed in aqueous solution to produce open chain aldehydic form and hence glucose pentaacetate does not react with NH2OH to form glucose oxime. The reactions are shown as:
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
What are monosaccharides?
Draw ring structure of α - D - (+) - glucopyranose.
Write the name of two monosaccharides obtained on hydrolysis of lactose sugar.
Write the product obtained when D-glucose reacts with H2N − OH.
Which one of the following is a monosaccharide:
starch, maltose, fructose, cellulose
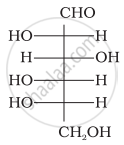
The letters ‘D’ or ‘L’ before the name of a stereoisomer of a compound indicate the correlation of configuration of that particular stereoisomer. This refers to their relation with one of the isomers of glyceraldehyde. Predict whether the following compound has ‘D’ or ‘L’ configuration.
Assertion: All naturally occurring α-aminoacids except glycine are optically active.
Reason: Most naturally occurring amino acids have L-configuration.
Naturally occurring glucose is called as ______.
