Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
How do you explain the amphoteric behaviour of amino acids?
उत्तर १
In aqueous solution, the carboxyl group of an amino acid can lose a proton and the amino group can accept a proton to give a dipolar ion known as zwitter ion.
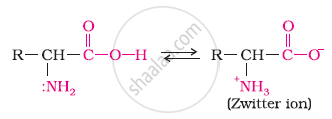
Therefore, in zwitter ionic form, the amino acid can act both as an acid and as a base.

Thus, amino acids show amphoteric behaviour.
उत्तर २
Amino acids contain an acidic (carboxyl group) and basic (amino group) group in the same molecule. In aqueous solution, they neutralize each other. The carboxyl group loses a proton while the amino group accepts it. As a result, a dipolar or zwitter ion is formed.

In zwitter ionjc form, a-amino acid show amphoteric behaviour as they react with both acids and bases.

APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Define the following term as related to proteins:
Primary structure
The functional group which is found in amino acids is:
Amino acids are the building blocks of ____________.
Amino acids are classified as acidic, basic or neutral depending upon the relative number of amino and carboxyl groups in their molecule. Which of the following are acidic?
(i)
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{(CH3)2CH - CH - COOH}\\
\phantom{..}|\\
\phantom{.....}\ce{NH2}
\end{array}\]
(ii)
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{HOOC - CH2 - CH2 - CH - COOH}\\
\phantom{............}|\\
\phantom{...............}\ce{NH2}
\end{array}\]
(iii)
\[\ce{H2N - CH2 - CH2 - CH2 - COOH}\]
(iv)
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{HOOC - CH2 - CH - COOH}\\
\phantom{.....}|\\
\phantom{........}\ce{NH2}
\end{array}\]
Assertion: Glycine must be taken through diet.
Reason: It is an essential amino acid.
Which of the following is an ester?
Which one of the following is an essential amino acid?
Draw the zwitter ion structure for sulphanilic acid.
Give a reason for the following observations:
Amino acids behave like salts.
