Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
How electricity is generated by using wind energy?
संक्षेप में उत्तर
उत्तर
- Wind is caused by the uneven heating of the atmosphere by the sun, variations in the earth's surface, and rotation of the earth. Mountains, bodies of water, and vegetation all influence wind flow patterns.
- Wind energy technologies use the energy in wind for practical purposes, such as generating electricity, charging batteries, pumping water, and grinding grain. Mechanical or electrical power is created through the kinetic energy of the wind. Wind power available is proportional to the cube of its speed, which means that the power available to a wind generator increases by a factor of eight if the wind speed doubles.
- Wind power is now the world's fastest growing energy source and the generation capacity has reached 435 GW at the end of 2015, around 7% of total global power generation capacity.
- Offshore wind has the potential to deliver substantial quantities of energy at a price that is cheaper than most of the other renewable energies, as wind speeds are generally higher offshore than on land.
Principle:
Wind turbines convert the kinetic energy in the wind into mechanical power. A generator can
convert mechanical power into electricity. The mechanical power can also be utilized directly
for specific tasks such as pumping water.
Construction and Working:
The basic components of the wind turbine include:
- a rotor, consists of the blades and the hub which convert the wind's energy into
rotational shaft energy - a nacelle containing a drive train, includes shafts, gearbox and generator
- pitch drive, turns the blades out of the wind to control rotor speed
- brake, slows the rotor down
- yaw drive, keeps the rotor and therefore the turbines facing the wind
- controller-anemometer, starts and stops the turbine from working depending on
conditions
a tower, to support the rotor and drive train; electronic equipment such as controls,
electrical cables, ground support equipment, and interconnection equipment.
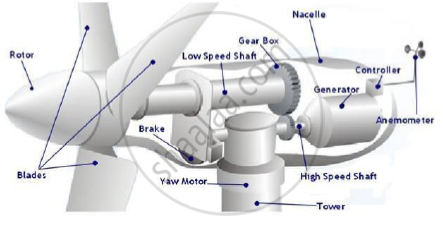
- The schematic of the wind turbine components are shown here.
When the wind blows a pocket of low-pressure air forms on the downwind side of
the blade. The low-pressure air pocket then pulls the blade toward it, causing the
rotor to turn. This is called lift. - The force of the lift is actually much stronger than the wind’s force against the front
side of the blade, which is called drag. The combination of lift and drag is what causes
the rotor to spin. - As the rotor spins, the low-speed shaft, which is connected to the gearbox, spins at
the same rate. - The gearbox takes this slow rotational speed and through correct gearing turns it into
a faster rotational speed. - The high-speed shaft, which is on the outgoing end of the gearbox and connected to
a generator, spins at a higher rate of speed. - The generator spins at this high rate of speed which spins magnets around a coil of
metal wire and generates electricity. - This electricity then travels down the tower to a transformer, where it is converted
again to AC or DC voltage depending on the grid.
shaalaa.com
Principle and Working with Wind Energy
क्या इस प्रश्न या उत्तर में कोई त्रुटि है?
