Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
उत्तर
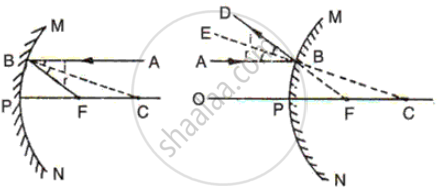
< i = < r
But < ABC = alternate< BCF
Therefore< CBF = < BCF
And the ΔFBC is isosceles
BF = FC ... (i)
PF = FC
PF + PF= PF + FC 2PF = PC
Now since PF = f, the focal length of the mirror
And PC = R, the radius of curvature of the mirror
From here we can determine the focal length of the concave mirror i.e. half of radius of curvature
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A ray of light is incident normally on a plane mirror. What will be the
angle of reflection?
What type of image is formed:
on a cinema screen?
Complete the following sentence:
All the distances are measured from the .......... of a spherical mirror.
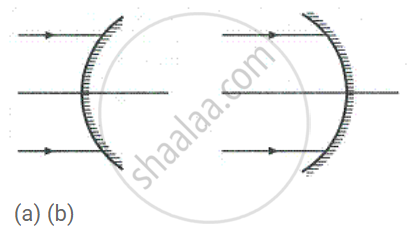
Name the mirrors shown in Figure (a) and (b).
What is meant by magnification? Write its expression. What is its sign for the (a) real (b) virtual, image?
Select the correct option:
Looking into a mirror one finds her image diminished, the mirror is:
Which of the following has curved reflecting surface?
If the focal length of a spherical mirror is 10 cm, what is the value of its radius of curvature?
Name the type of mirror used in the following situation:
Side/rear-view mirror of a vehicle
Support your answer with reason.
Name the type of mirror used in the following situation:
Solar furnace
Support your answer with reason.
