Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
If the price of a substitute Y of good X increases, what impact does it have on the equilibrium price and quantity of good X?
उत्तर
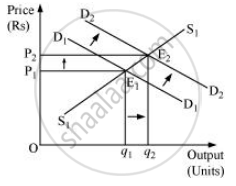
X and Y being substitute goods, if the price of Y increases, then it will reduce the demand for Y and people will switch to X, which will raise the demand for X. Thus, the demand curve will shift from D1D1 to D2D2 . At the existing price P1, there will be an excess demand. Due to the pressure of excess demand, the existing price will increase. Consequently, the new equilibrium occurs at E2, where the new demand curve D2D2 intersects the supply curve S1S1. The new equilibrium price is P2, which is higher than P1 and equilibrium quantity is q2, which is higher than q1. Therefore, due to the increase in the price of substitute good Y, the equilibrium price of X will rise and equilibrium output of X will also be higher.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Determination of equilibrium price under perfect competition.
Explain the chain effects, if the prevailing market price is below the equilibrium price.
Giving reason, state whether the following statement is true or false.
When equilibrium price of a good is less than its market price, there will be competition among the sellers.
X and Y are complementary goods. The price of Y falls. Explain the chain of effects of this change in the market of X.
Explain the chain of an effect of excess demand of a good on it equilibrium price.
Equilibrium price of an essential medicine is too high. Explain what possible steps can be taken to bring down the equilibrium price but only through the market forces. Also explain the series of changes that will occur in the market.
Write explanatory answer.
Define perfect competition and explain price determination under perfect competition.
Suppose the price at which the equilibrium is attained in exercise 5 is above the minimum average cost of the firms constituting the market. Now if we allow for free entry and exit of firms, how will the market price adjust to it?
At what level of price do the firms in a perfectly competitive market supply when free entry and exit is allowed in the market? How is the equilibrium quantity determined in such a market?
Define or explain the following concept:
Equilibrium price
State whether the following statement is TRUE and FALSE.
Under perfect competition, price is determined by equilibrium of demand and supply.
Fill in the blank with appropriate alternative given below
The price at which demand and supply equate to each other is called _______ price.
Suppose the demand and supply equations of a commodity X in a perfectly competitive market are given by :
Qd = 1700 – 2P
Qs = 1300 + 3P
Calculate the value of equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity of the commodity X.
State whether the following statement is true or false. Give reasons for your answer :
When the equilibrium price is greater than the market price there will be excess supply in the market.
Answer the following question:
The market for a good is in equilibrium. How would an increase in an input price affect the equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity, keeping other factors constant? Explain using a diagram.
