Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
If the Earth’s pull on the Moon suddenly disappears, what will happen to the Moon?
उत्तर
Earth’s pull is, F = `("GM"_"E""M"_"m")/("R"_"m"^2)`
The moon will move away with the largest distance of approach. The motion of the moon would cease.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A planet moving along an elliptical orbit is closest to the Sun at distance r1 and farthest away at a distance of r2. If v1 and v2 are linear speeds at these points respectively. Then the ratio `"v"_1/"v"_2` is
The gravitational potential energy of the Moon with respect to Earth is ____________.
Write unit of the gravitational field.
What is meant by the superposition of the gravitational field?
Is potential energy the property of a single object? Justify.
Define gravitational potential.
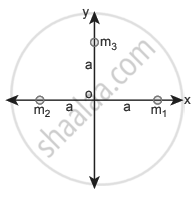
Calculate the gravitational field at point O due to three masses m1, m2 and m3 whose positions are given by the following figure. If the masses m1 and m2 are equal what is the change in a gravitational field at the point O?
What is the gravitational potential energy of the Earth and Sun? The Earth to Sun distance is around 150 million km. The mass of the Earth is 5.9 × 1024 kg and the mass of the Sun is 1.9 × 1030 kg.
Earth revolves around the Sun at 30 km s−1. Calculate the kinetic energy of the Earth. In the previous example, you calculated the potential energy of the Earth. What is the total energy of the Earth in that case? Is the total energy positive? Give reasons.
An object is thrown from Earth in such a way that it reaches a point at infinity with non-zero kinetic energy `["K"."E"("r" = ∞) = 1/2 "Mv"_"∞"^2]`, with what velocity should the object be thrown from Earth?
