Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
If unit of rate constant is mol dm−3s−1, the order of reaction would be ______.
विकल्प
zero
1
2
3
उत्तर
If unit of rate constant is mol dm−3s−1, the order of reaction would be zero.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The decomposition of NH3 on platinum surface is zero order reaction. What are the rates of production of N2 and H2 if k = 2.5 × 10−4 mol−1 L s−1?
Give one example of zero order reaction.
For which of the following reaction the units of rate constant and rate of the reaction are same?
At high pressure the following reaction is zero order.
\[\ce{2NH3(g) ->[1130 K][Platinum catalyst] N2(g) + 3H2(g)}\]
Which of the following options are correct for this reaction?
(i) Rate of reaction = Rate constant.
(ii) Rate of the reaction depends on concentration of ammonia.
(iii) Rate of decomposition of ammonia will remain constant until ammonia disappears completely.
(iv) Further increase in pressure will change the rate of reaction.
Which of the following graphs is correct for a zero order reaction?
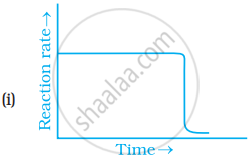
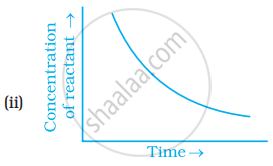
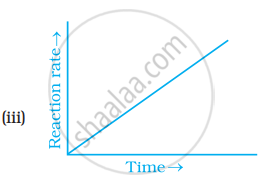

Write the rate equation for the reaction `2A + B -> C` if the order of the reaction is zero.
For a zero order reaction will the molecularity be equal to zero? Explain.
A solution with initial concentration of a mol dm-3 follow zero order kinetic. The time taken for the completion of reaction is
Consider the following statement:-
(i) Increase in concentration of reactant increases the rate of a zero-order reaction.
(ii) Rate constant k is equal to collision frequency A if Ea = 0
(iii) Rate constant k is equal to collision frequency A if Ea = 0
(iv) In k vs t is a straight line
(v) In k vs 1/T is a straight line
Which of the above statement is correct?
For a zero-order reaction, the plot of [A]t vs t is linear with a ______
Write the expression of integrated rate equation for zero order reaction.
The slope in the plot of [R] Vs. time for a zero-order reaction is ______.
The following experimental rate data were obtained for a reaction carried out at 25°C:
\[\ce{A_{(g)} + B_{(g)} -> C_{(g)} + A_{(g)}}\]
| Initial [A(g)]/mol dm−3 | Initial [B(g)]/mol dm−3 | Initial rate/mol dm−3s−1 |
| 3.0 × 10−2 | 2.0 × 10−2 | 1.89 × 10−4 |
| 3.0 × 10−2 | 4.0 × 10−2 | 1.89 × 10−4 |
| 6.0 × 10−2 | 4.0 × 10−2 | 7.56 × 10−4 |
What are the orders with respect to A(g) and B(g)?
If the initial concentration of substance A is 1.5 M and after 120 seconds the concentration of substance A is 0.75 M, the rate constant for the reaction if it follows zero-order kinetics is ______.
What is zeroth order reaction? Derive its integrated rate Law. What are the units of rate constant?
Derive the expression for integrated rate law for zero order reaction A → Products.
Write the unit of rate constant of zero order reaction.
What is zero order reaction?
