Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
In a shotput event an athlete throws the shotput of mass 10 kg with an initial speed of 1 ms–1 at 45° from a height 1.5 m above ground. Assuming air resistance to be negligible and acceleration due to gravity to be 10 ms–2, the kinetic energy of the shotput when it just reaches the ground will be ______.
विकल्प
2.5 J
5.0 J
52.5 J
155.0 J
उत्तर
In a shotput event an athlete throws the shotput of mass 10 kg with an initial speed of 1 ms–1 at 45° from a height 1.5 m above ground. Assuming air resistance to be negligible and acceleration due to gravity to be 10 ms–2, the kinetic energy of the shotput when it just reaches the ground will be 155.0 J.
Explanation:
If air resistance is negligible, the total mechanical energy of the system will remain constant. And let us take the ground as a reference where potential energy will be zero.
According to the problem, h = 1.5 m, v = 1 m/s, m = 10 kg, g = 10 ms– 2
The initial energy of the shotput = `(PE)_i + (KE)_i`
= `mgh + 1/2 mv^2`
= `10 xx 10 xx 1.5 + 1/2 xx 10 xx (1)^2`
= 150 + 5
= 155 J
From the conservation of mechanical energy,
`(PE)_i + (KE)_i = (PE)_f + (KE)_f`
⇒ `155_j = 0 + (KE)_f`
So, the final kinetic energy of the shotput is 155 J.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A body is initially at rest. It undergoes one-dimensional motion with constant acceleration. The power delivered to it at time t is proportional to ______.
A heavy stone is thrown in from a cliff of height h in a given direction. The speed with which it hits the ground
(a) must depend on the speed of projection
(b) must be larger than the speed of projection
(c) must be independent of the speed of projection
(d) may be smaller than the speed of projection.
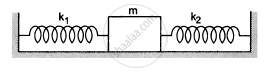
A block of mass m is attached to two unstretched springs of spring constants k1 and k2 as shown in the following figure. The block is displaced towards the right through a distance x and is released. Find the speed of the block as it passes through the mean position shown.
In the following figure shows two blocks A and B, each of mass of 320 g connected by a light string passing over a smooth light pulley. The horizontal surface on which the block Acan slide is smooth. Block A is attached to a spring of spring constant 40 N/m whose other end is fixed to a support 40 cm above the horizontal surface. Initially, the spring is vertical and unstretched when the system is released to move. Find the velocity of the block A at the instant it breaks off the surface below it. Take g = 10 m/s2.
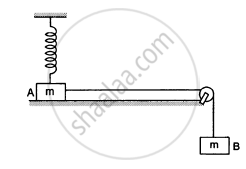
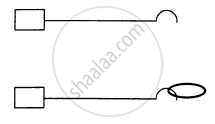
Figure following shows a light rod of length l rigidly attached to a small heavy block at one end and a hook at the other end. The system is released from rest with the rod in a horizontal position. There is a fixed smooth ring at a depth h below the initial position of the hook and the hook gets into the ring as it reaches there. What should be the minimum value of h so that the block moves in a complete circle about the ring?
A particle is released from height S from the surface of the Earth. At a certain height, its kinetic energy is three times its potential energy. The height from the surface of the earth and the speed of the particle at that instant are respectively ______.
Two inclined frictionless tracks, one gradual and the other steep meet at A from where two stones are allowed to slide down from rest, one on each track as shown in figure.
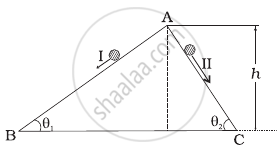
Which of the following statement is correct?
Which of the diagrams shown in figure represents variation of total mechanical energy of a pendulum oscillating in air as function of time?
Why is electrical power required at all when the elevator is descending? Why should there be a limit on the number of passengers in this case?
A bob of mass m suspended by a light string of length L is whirled into a vertical circle as shown in figure. What will be the trajectory of the particle if the string is cut at
- Point B?
- Point C?
- Point X?

