Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
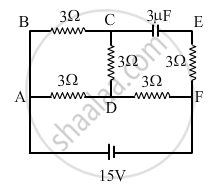
In the circuit shown in the figure, find the total resistance of the circuit and the current in the arm AD.
उत्तर
Since the capacitor will act as an open circuit here, the arm CE and EF will become ineffective. The circuit is now reduced to as below

Effective resistance across AD = (BC + CD) ∥ AD
= \[\left( 3 + 3 \right) \lVert 3 = 2 \Omega\]
Total resistance of the circuit = AD + DF = 2 + 3 = 5 Ω
Total current in the circuit = \[\frac{15}{5} = 3 A\]
The current through AD and BCD will divide in the inverse ratio of the resistance.
∴ Current through AD = \[3 \times \frac{6}{\left( 6 + 3 \right)} = 3 \times \frac{6}{9} = 2 A\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A low voltage supply from which one needs high currents must have very low internal resistance. Why?
Fill in the following blank with suitable words:
Resistance is measured in .............. The resistance of a wire increases as the length ..............; as the temperature ..............; and as the cross-sectional area .............. .
In a conductor 6.25 × `10^16` electrons flow from its end A to B in 2 s. Find the current flowing through the conductor (e = 1.6 × `10^-19` C)
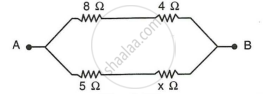
In the circuit shown below in Fig, calculate the value of x if the equivalent resistance between A and B is 4 Ω.
Rewrite the following statement by selecting the correct option.
The S.I. unit of resistance is __________.
What are non-ohmic conductors? Give one exmaple. Draw a current-voltage graph for a non-ohmic conductor.
The ratio of the potential difference to the current is known as ________.
Write a short note on superconductors?
