Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
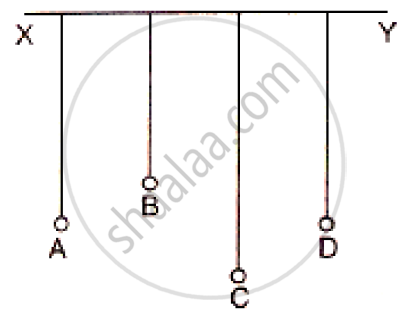
In following figure shows A, B, C and D are four pendulums suspended from the same elastic string XY. Lengths of pendulum A and D are equal, while the length of pendulum B is smaller and the pendulum C is longer. The pendulum A is set into vibration.
(a) what is your observation? (b) Give reason for your observation.
उत्तर
(a) Set the pendulum A into vibration by displacing it to one side, normal to its length. It is observed that pendulum D also starts vibrating initially with a small amplitude and ultimately it acquires the same amplitude as the pendulum A initially had. When the amplitude of the pendulum D becomes maximum, the amplitude of the pendulum A becomes minimum since the total energy is constant. After some time the amplitude of the pendulum D will decreases and amplitude of A increases. The exchange of energy takes place only between the pendulums A and D because their natural frequencies are same. The pendulums B and C also vibrate, but with very small amplitudes.
(b) The vibrations produced in pendulum A are communicated as forced vibrations to the other pendulums B, C and D through XY. The pendulums B and C remain in the state of forced vibrations, while the pendulum D comes in the state of resonance.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Resonance is a special case of ______ vibrations, when frequency of the driving force is ______ natural frequency of the body.
In following figure shows two tuning forks A and B of the same frequency mounted on two separate sound boxes with their open ends facing each other. The fork A is set into vibration.
- Describe your observation.
- State the principle illustrated by this experiment.

Two pendulums C and D are suspended from a wire as shown in the figure give below. Pendulum C is made to oscullate by displaying it from its mean position. It is seen that D also starts oscillating.
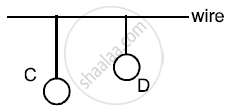
(i) Name the type of oscillation, C will execute.
(ii) Name the type of oscillation, D will execute.
(iii) If the length of D is made equal to C then what difference will you notice in the oscillations of D ?
(iv) What is the name of the phenomenon when the length of D is made equal to C ?
Differentiate between the following:
Radio waves and light waves.
What do you mean by resonance? When does resonance occur?
Explain a tuning fork (vibrating) is held close to ear. One hears a faint sound. The same vibrating tuning fork is placed on table, such that its handle is in contact with table, one hears a loud sound.
Explain a person walking past a railway line, in the middle of night hears a ringing sound along with the sound of his footsteps.
What do you understand by free vibrations of a body? Draw a displacement-time graph to represent them. Given one example.
