Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
In hydra the type of reproduction is ___________.
विकल्प
Binary fission
Budding
Multiple fission
None of the above
उत्तर
In hydra the type of reproduction is Budding.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Explain the process of regeneration in Planaria.
How are the modes for reproduction different in unicellular and multicellular organisms?
Define asexual reproduction.
What happens when Bryophyllum leaf falls on the wet soil?
Name the asexual method of reproduction in Hydra
Name the natural method by which strawberry plants are propagated.
Fill in the following blank with suitable word :
Vegetative reproduction of potato plants is done by using ............
Fill in the following blank with suitable word :
Strawberry plants are propagated by the natural............... method.
Name two plants which are usually propagated by artificial propagation methods. Name the method of artificial propagation used in each case.
Name two marine organisms which also reproduce by the same method as yeast but form colonies.
Name two fruit trees which are usually propagated by grafting method.
One of the following organisms does not reproduce by binary fission. This is :
(a) Amoeba
(b) Plasmodium
(c) Leishmania
(d) Paramecium
The micro-organism which reproduces by multiple fission is the one which causes the disease known as :
(a) Kala-azar
(b) marasmus
(c) malaria
(d) amoebiasis
One of the following organisms does not reproduce by budding. This is :
(a) Sponge
(b) Yeast
(c) Hydra
(d) Planaria
One of the following organisms does not reproduce by fission. This is :
(a) Amoeba
(b) Leishmania
(c) Planaria
(d) Plasmodium
There are four tiny organisms A, B, C and D. The organism A is a parasitic protozoan which causes a disease known as kala-azar. The organism B is a microscopic single-celled animal which causes malaria disease in human beings. The organism C is a unicellular animal which can change its body shape according to need, it has no fixed shape. The organism D is also a unicellular animal which is slipper-shaped having a large number of tiny hair all around its body.
(a) Name the organisms A, B, C and D
(b) Name one characteristic body feature of organism A.
(c) Name the insect which carries organism B and transmits it from one person to another.
(d) What name is given to the asexual method of reproduction of (i) organism A, and (ii) organism B?
(e) Where do organisms C and D live?
Fill in the following blank with suitable word :
The process of fusion of gametes is called .............
With the help of suitable diagram, describe Binary fission in plants.
Fill in the blank:
Budding is a kind of _________ reproduction.
Fill in the blank:
Amoeba reproduces by _________.
Mention the common method of reproduction in Bougainvillea.
A student after observing a slide showing different stages of binary fission in Amoeba draws the following diagrams. However these diagrams are not in proper sequence: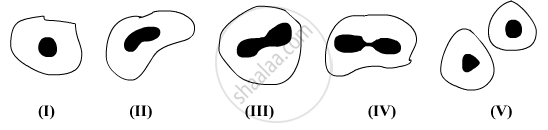
The correct sequence is:
(A) I, V, IV, III, II
(B) I, III, IV, V, II
(C) I, V, III, IV, II
(D) I, IV, V, III, II
Explain the term Vegetative propagation.
Name four plants which can be propagated by stem-cutting.
Name the parts of the plants used to grow following flower: Lily
What is micropropagation?
A method in which roots are induced on the stem while it is still attached to the parent plant is called
Grafting is not possible in the monocots because they
Asexual reproduction occurs by __________ cell division.
Distinguish between the following.
Binary fission and Multiple fission
Seeds are the product of asexual reproduction.
Asexual reproduction is also known as ______.
Offspring formed by the asexual method of reproduction have greater similarities among themselves because ______
(i) asexual reproduction involves only one parent
(ii) asexual reproduction does not involve gametes
(iii) asexual reproduction occurs before sexual reproduction
(iv) asexual reproduction occurs after sexual reproduction
In Spirogyra, asexual reproduction takes place by ______
Mustard was growing in two fields- A and B. While Field A produced brown coloured seeds, field B produced yellow coloured seeds.
It was observed that in field A, the offsprings showed only the parental trait for consecutive generations, whereas in field B, majority of the offsprings showed a variation in the progeny.
What are the probable reasons for these?
When one of the following is correctly matched?
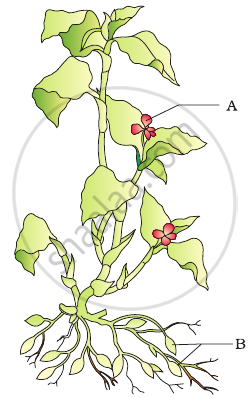
In the figure given below the plant bears two different types of flowers marked ‘A’ and ‘B’. Identify the types of flowers and state the type of pollination that will occur in them.
What do the following parts of a flower develop into after fertilisation?
| a. | Ovary | ______ |
| b. | Ovules | ______ |
