Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
It is sometimes observed that the F1 progeny has a phenotype that does not resemble either of the two parents and has an intermediate phenotype. Explain by taking a suitable example and working out the cross upto F2 progeny.
उत्तर
It's called incomplete dominance or partial dominance when a heterozygote has a phenotype that falls between the two homozygous parents. Snapdragons' blossom colour serves as a perfect example of incomplete dominance.
Two alleles make up the flower colour gene in snapdragons: the red allele (R) and the white allele (W). The red allele is dominant, whereas the white allele is recessive. The homozygous white snapdragon (WW) will have white flowers, but the homozygous red snapdragon (RR) will have red blooms.
If a homozygous red snapdragon (RR) and a homozygous white snapdragon (WW) are crossed to produce a heterozygous snapdragon (RW), the F1 generation will have pink flowers, which are a mid-phenotype between red and white. This is due to the fact that the heterozygote's flower colour is expressed by both the red and white alleles, resulting in a blending of the two colours.

Monohybrid cross in Snapdragon, where one allele is incompletely dominant over the other allele.
संबंधित प्रश्न
Mendel published his work on inheritance of characters in 1865, but it remained unrecognised till 1900. Give three reasons for the delay in accepting his work.
Mention the Phenotype and Genotype ratios of the offspring in F2 generation.
State the three Mendel’s laws of inheritance.
Predict the genotype and phenotype of the following cross in pea.
tt x TT
(Capital letters show dominance)
A family consists of two parents and their five children and the pedigree chart below shows the inheritance of the trait colour blindness .
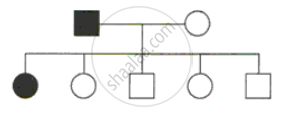
(i) Who is colour blind in parents - Father or Mother?
(ii) How many daughters and sons have beeen born in the family?
(iii) What does the child 1 indicate about this trait?
(iv) Complete the depiction of all probabilities of the trait among the children 2-5 in the chart.
(v) On which chromosome is the gene of this trait located?
(vi) Name one other trait in humans which follows the similar mode of inheritance.
______ pairs of contrasting traits were studied by Mendel in pea plant.
Which of the following crosses will give tall and dwarf pea plants in same proportions?
Two pea plants one with round green seeds (RRyy) and another with wrinkled yellow (rrYY) seeds produce F1 progeny that have round, yellow (RrYy) seeds. When F1 plants are selfed, the F2 progeny will have new combination of characters. Choose the new combination from the following:
- Round, yellow
- Round, green
- Wrinkled, yellow
- Wrinkled, green
Read the following and answer from given below:
According to Mendel, one gene controls the expression of one character only. The ability of a gene to have multiple phenotypic effects because it influences a number of characters are an exception. The gene has multiple phenotypic effects because its ability to control two or more characters can be seen in cotton. In cotton, a gene for the lint also influences the height of the plant, size of the ball, number of ovules, and viability of seeds.
Which of the following statements is not correct regarding genes with multiple phenotypic effects?
Which one of the following cannot be explained on the basis of Mendel’s Law of Dominance?
