Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Keeping the p.d. constant, the resistance of a circuit is halved. The current will become:
(a) one-fourth
(b) four time
(c) half
(d) double
उत्तर
d) double
As we know from Ohm’s law:
Voltage = Current x Resistance
V = IR
If the voltage is constant, the resistance of the circuit is halved. That is, it becomes R / 2.
Current, I = V/R
I = V/R
I = V/R/2 = 2 I
Thus by keeping the p.d. constant, the resistance of a circuit is halved and the current is doubled.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The relationship between the potential difference and the current in a conductor is stated in the form of a law.
1) Name the law.
2) What does the slope of V-I graph for a conductor represent?
3) Name the material used for making the connecting wire.
Name the law which is illustrated by the above V−I graph.
In an experiment of verification of Ohm’s law following observations are obtained.
|
Potential difference V (in volt) |
0.5 | 1.0 | 1.5 | 2.0 | 2.5 |
| current I (in ampere) | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 1.0 |
Draw a V-I graph and use this graph to find:
- the potential difference V when the current I is 0.5 A,
- the current I when the potential difference V is 0.75 V,
- the resistance in a circuit.
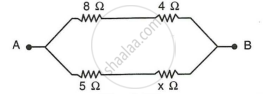
In the circuit shown below in Fig, calculate the value of x if the equivalent resistance between A and B is 4 Ω.
- Name and state the law which relates the potential difference and current in a conductor.
- What is the necessary condition for a conductor to obey the law named above in part (a) ?
What is meant by the drift speed of free electrons?
SI unit of resistance is:
The temperature of a conductor is increased. The graph best showing the variation of its resistance is:
Why should an ammeter have low resistance?
