Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Let us list some of the factors, which could possibly influence the speed of wave propagation:
(i) Nature of the source
(ii) Direction of propagation
(iii) Motion of the source and/or observer
(iv) Wavelength
(v) Intensity of the wave
On which of these factors, if any, does the speed of light in vacuum?
उत्तर
The speed of light in a vacuum i.e., 3 × 108 m/s (approximately) is a universal constant. It is not affected by the motion of the source, the observer, or both. Hence, the given factor does not affect the speed of light in a vacuum.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The refractive index of glass is 1.5. What is the speed of light in glass? (Speed of light in vacuum is 3.0 × 108 m s−1)
Is the speed of light in glass independent of the colour of light? If not, which of the two colours red and violet travels slower in a glass prism?
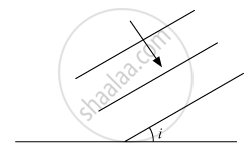
A plane wavefront propagating in a medium of refractive index 'μ1' is incident on a plane surface making the angle of incidence 'i' as shown in the figure. It enters into a medium of refractive index 'μ2' (μ2 > μ1). Use Huygens' construction of secondary wavelets to trace the propagation of the refracted wavefront. Hence verify Snell's law of refraction.
The wavefronts of a light wave travelling in vacuum are given by x + y + z = c. The angle made by the direction of propagation of light with the X-axis is _________ .
Light waves travel from optically rarer medium to optically denser medium. Its velocity decreases bec;ause of change in ______.
The optical properties of a medium are governed by the relative permittivity (εr) and relative permeability (µr). The refractive index is defined as `sqrt(µ_r ε_r) = n`. For ordinary material εr > 0 and µr > 0 and the positive sign is taken for the square root. In 1964, a Russian scientist V. Veselago postulated the existence of material with εr < 0 and µr < 0. Since then such ‘metamaterials’ have been produced in the laboratories and their optical properties studied. For such materials `n = - sqrt(µ_r ε_r)`. As light enters a medium of such refractive index the phases travel away from the direction of propagation.
- According to the description above show that if rays of light enter such a medium from air (refractive index = 1) at an angle θ in 2nd quadrant, them the refracted beam is in the 3rd quadrant.
- Prove that Snell’s law holds for such a medium.
In the figure, the optical fibre is l = 2 m long and has a diameter of d = 20 µm. If a ray of light is incident on one end of the fiber at angle θ1 = 40°, the number of reflections it makes before emerging from the other end is close to ______.
(Refractive index of fiber is 1.31 and sin40° = 0.64)

A glass slab of thickness 4 cm contains the same number of waves as 5 cm of water. When both are traversed by the same monochromatic light. If the refractive index of water is `(4/3)`. What is that of glass?
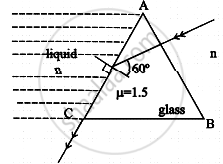
In the given figure, the face AC of the equilateral prism is immersed in a liquid of refractive index 'n'. For incident angle 60° at the side AC, the refracted light just grazes along face AC. The refractive index of the liquid n = `sqrtx/4`. The value of x is ______.
(Given refractive index of glass = 1.5)
White light is an incident at 20° on a material of silicate flint glass slab as shown. `μ_"violet"` = 1.66 and µr = 1.6. For what value of d will the separation be 1 mm in red and violet rays?

A light ray in a medium (RI = 5/3) enters another medium at an angle of 30°. The angle in the other medium is sin-1 (5/6). The incident angle must be increased such that the ray is completely reflected at minimum degrees is ______.
Using Huygens’s construction of secondary wavelets draw a diagram showing the passage of a plane wavefront from a denser to a rarer medium. Using it verifies Snell’s law.
