Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Match the items in Column A with those in Column B.
|
Column A |
Column B |
|
(a) Generative nucleus |
(i) Pollen tube |
|
(b) Germ pore |
(ii) Endosperm nucleus |
|
(c) Exine |
(iii) Testa |
|
(d) Secondary nucleus |
(iv) Fertilization |
|
(e) Integument |
(v) Male nuclei |
|
(f) Egg nucleus |
(vi) Rough |
उत्तर
|
Column A |
Column B |
|
(a) Generative nucleus |
(i) Male nuclei |
|
(b) Germ pore |
(ii) Pollen tube |
|
(c) Exine |
(iii) Rough |
|
(d) Secondary nucleus |
(iv) Endosperm nucleus |
|
(e) Integument |
(v) Testa |
|
(f) Egg nucleus |
(vi) Fertilization |
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
What happens to the following after fertilization?
Calyx
What is polyembryony? How it can commercially exploited.
Write a short note on Pollen kitt.
Following diagram represents double fertilization. Identify the INCORRECT label.
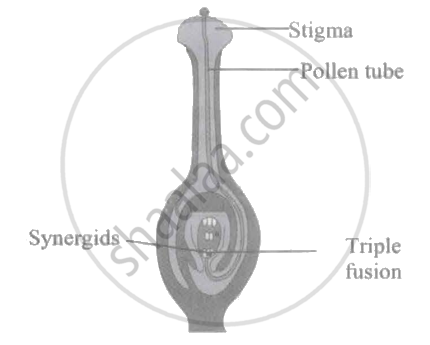
In a fertilised embryo sac, the haploid, diploid, and triploid structures are ______.
The total number of nuclei involved in double fertilisation in angiospersm are ______.
In ______ sepal is seen on the fruit after fertilization.
Can an unfertilised, apomictic embryo sac give rise to a diploid embryo? If yes, then how?
Which are the three cells found in a pollen grain when it is shed at the three celled stage?
Name the following:
A diploid nucleus in central cell of embryo sac in plants.
