Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Match the pairs.
| ‘A’ Group | ‘B’ Group |
| 1. Free electrons | a. V/R |
| 2. Current | b. Increases the resistance in the circuit |
| 3. Resistivity | c. Weakly attached |
| 4. Resistances in series | d. VA/LI |
उत्तर
| ‘A’ Group | Answer |
| 1. Free electrons | c. Weakly attached |
| 2. Current | a. V/R |
| 3. Resistivity | d. VA/LI |
| 4. Resistances in series | b. Increases the resistance in the circuit |
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Why are metals good conductors of electricity whereas glass is a bad conductor of electricity? Give reason?
State the factors on which the strength of electric current flowing in a given conductor depends.
An electric circuit consisting of a 0.5 m long nichrome wire XY, an ammeter, a voltmeter, four cells of 1.5 V each and a plug key was set up.
Following graph was plotted between V and I values:
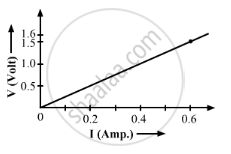
What would be the values of `V/I` rations when the potential difference is 0.8 V, 1.2 V and 1.6 V respectively?
What conclusion do you draw from these values?
What is the resistance of the wire?
The p.d. across a 3 Ω resistor is 6 V. The current flowing in the resistor will be:
(a) `1/2A`
(b) 1 A
(c) 2 A
(d) 6 A
For a heater rated at 4 kW and 220 V, calculate:
(a) the current,
(b) the resistance of the heater,
(c) the energy consumed in 2 hours, and
(d) the cost if 1 kWh is priced at Rs 4.60.
State the relation between work, charge and potential difference for an electric circuit.
Two resistors P and Q of the same material and length but of different thickness are connected in parallel to a battery. The cross- sectional area of P is twice that of Q. What is the ratio of
(a) The resistance of P to the resistance of Q?
(b) The current in P to the current in Q?
What is the purpose of fuse in an electrical circuit?
60 joules of heat was dissipated in a resistor when 20 C flowed for 5 s. Calculate:
(a) P.d. across the resistor,
(b) Resistance of the resistor, and
(c) Average power dissipated in the resistor.
The circuit diagram in fig shows two coils of an insulated copper wire wound on a cardboard tube. G is a center zero galvanometer.
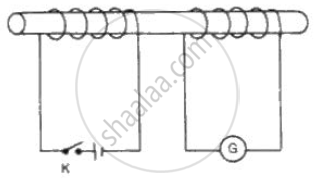
(a) Describe what will happen when th e swi tch K is cl osed for severa l
seconds and then opened again .
(b) What will be the effect of repeating the experiment with an iron placed in the tube?
A bulb marked 12 V, 24 W operates on a 12 V battery for 20 minutes. Calculate:
- The current flowing through it, and
- The energy consumed.
A geyser is rated 1500 W, 250 V. This geyser is connected to 250 V mains. Calculate:
- The current drawn,
- The energy consumed in 50 hours, and
- The cost of energy consumed at ₹ 4.20 per kWh.
Answer the following question.
What is the function of a galvanometer in a circuit?
In current electricity, a positive charge refers to ______.
