Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Match the quantum numbers with the information provided by these.
| Quantum number | Information provided |
| (i) Principal quantum number | (a) orientation of the orbital |
| (ii) Azimuthal quantum number | (b) energy and size of orbital |
| (iii) Magnetic quantum number | (c) spin of electron |
| (iv) Spin quantum number | (d) shape of the orbital |
उत्तर
| Quantum number | Information provided |
| (i) Principal quantum number | (b) energy and size of orbital |
| (ii) Azimuthal quantum number | (d) shape of the orbital |
| (iii) Magnetic quantum number | (a) orientation of the orbital |
| (iv) Spin quantum number | (c) spin of electron |
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Using s, p, d notations, describe the orbital with the following quantum numbers n = 1, l = 0.
Choose the correct option.
p-orbitals are _________ in shape.
Choose the correct option.
“No two electrons in the same atoms can have identical set of four quantum numbers”. This statement is known as -
Write condensed orbital notation of electronic configuration of the following element:
Silicon (Z = 14)
How many electrons in 19K have n = 3, l = 1?
The probability density plots of 1s and 2s orbitals are given in Figure:
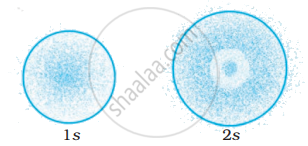
The density of dots in a region represents the probability density of finding electrons in the region.
On the basis of above diagram which of the following statements is incorrect?
The number of radial nodes for 3p orbital is ______.
In which of the following pairs, the ions are iso-electronic?
(i) \[\ce{Na^{+}, Mg^{2+}}\]
(ii) \[\ce{Al3^{+}, O-}\]
(iii) \[\ce{Na+ , O2-}\]
(iv) \[\ce{N3-, Cl-}\]
The arrangement of orbitals on the basis of energy is based upon their (n + l) value. Lower the value of (n + l), lower is the energy. For orbitals having same values of (n + l), the orbital with lower value of n will have lower energy.
Based upon the above information, arrange the following orbitals in the increasing order of energy.
5p, 4d, 5d, 4f, 6s
The arrangement of orbitals on the basis of energy is based upon their (n + l) value. Lower the value of (n + l), lower is the energy. For orbitals having same values of (n + l), the orbital with lower value of n will have lower energy.
Based upon the above information, arrange the following orbitals in the increasing order of energy.
5f, 6d, 7s, 7p
