Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
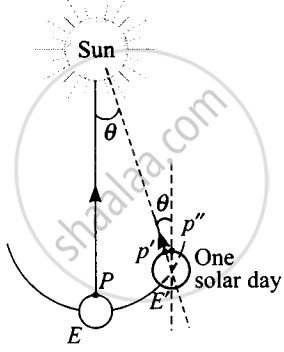
Mean solar day is the time interval between two successive noon when sun passes through zenith point (meridian). Sidereal day is the time interval between two successive transit of a distant star through the zenith point (meridian). By drawing appropriate diagram showing earth’s spin and orbital motion, show that mean solar day is four minutes longer than the sidereal day. In other words, distant stars would rise 4 minutes early every successive day.
उत्तर
According to the diagram alongside, when the earth revolves about its polar axis in one sidereal day, it also moves from E to E’ around the sun due to translational motion and the point P’ is at P’’.
When the Earth still rotates through an angle about its axis to complete one solar day until the point P’ is at P”, again facing the sun.
Earth advances in its orbit by approximately 1° every day, i.e. in 24 hours. Then, it will have to rotate by 361° (which we define as 1 day) to have the sun at the zenith point again,
∴ Time is taken to traverse `1^circ`
= `(24h)/(361^circ) xx 1^circ`
= `(24 xx 60 xx 60s)/361`
= 239.3s
i.e., 239.3s = 3 min 59.3s ≈ 4 min
Hence, distant stars would rise 4 minutes early every successive day.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
As you have learnt in the text, a geostationary satellite orbits the earth at a height of nearly 36,000 km from the surface of the earth. What is the potential due to earth’s gravity at the site of this satellite? (Take the potential energy at infinity to be zero). Mass of the earth = 6.0 × 1024 kg, radius = 6400 km
Choose the INCORRECT statement about geostationary satellite.
Which of the following are true?
- A polar satellite goes around the earth’s pole in north- south direction.
- A geostationary satellite goes around the earth in east-west direction.
- A geostationary satellite goes around the earth in west-east direction.
- A polar satellite goes around the earth in east-west direction.
What is the angle between the equatorial plane and the orbital plane of polar satellite?
What is the angle between the equatorial plane and the orbital plane of geostationary satellite?
A satellite is to be placed in equatorial geostationary orbit around earth for communication.
- Calculate height of such a satellite.
- Find out the minimum number of satellites that are needed to cover entire earth so that at least one satellites is visible from any point on the equator.
[M = 6 × 1024 kg, R = 6400 km, T = 24 h, G = 6.67 × 10–11 SI units]
