Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Mendel crossed a homozygous pea plant having round seeds (RR) with a homozygous pea plant having wrinkled seeds (rr). He got different results. On the basis of it, answer the following questions:
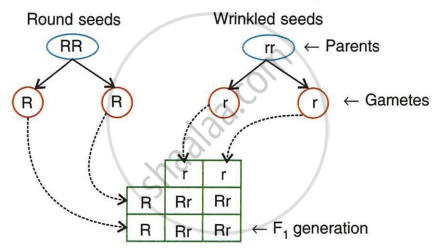
- Which character of seed is studied in the experiment?
- Which of the above two traits is dominant?
- Write the phenotype and genotype of F1 offspring.
- Mention and state Mendel's law as shown in the above cross.
- Make a Punnett square for F2 generation when two plants of F1 offspring are crossed with each other.
- Write the phenotypic ratio of F2 progeny.
- What will be the genotypic ratio of F2 offspring?
- What are the two traits of seed colour ? Also mention which is dominant and recessive?
- Write the scientific name of the garden pea.
- Write two main features of the pea plant, due to which Mendel selected it for his hybridisation studies.
उत्तर
- The experiment is looking at the seed's form.
- Most prevalent is the round-shaped character.
- Phenotype: All F1 offspring have round seeds.
Genotype: All F1 offspring have the genotype Rr, representing a heterozygous combination of one dominant allele (R) and one recessive allele (r) for seed shape. - Mendel's Law of Dominance: Out of a pair of opposing personalities present together, only one is able to express herself while the other stays repressed.
R r R RR Rr r Rr rr - Phenotypic ratio : 3 : 1
- Genotypic ratio : 1 : 2 : 1
- Yellow and green are the colours of seeds. Green is recessive; yellow is dominant.
- Pisum Sativum
- Mendel had chosen garden peas for the following purposes:
- There were several variants accessible as different forms of a character.
- Varieties were accessible in pure forms that bred true, that is, produced the same type generation after generation.
- Normally self-pollinated, removal of the relevant reproductive elements (male stamens and female carpels) of the flower could inhibit self-pollination and could as well be cross-pollinated artificially.
- A pea plant has a short lifetime; hence, several generations can be obtained and investigated in less time.
संबंधित प्रश्न
Which one of the following genotypes is homozygous dominant and which one homozygous recessive in regards to tongue rolling:
In a certain species of animals, black fur (B) is dominant over brown fur (b) Predict the genotype and phenotype of the offspring when both parents are ‘Bb’ or have heterozygous
black fur .
The physical expression of a character is called ______.
Distinguish between the following pair:
Homozygous and Heterozygous chromosomes
A homozygous plant having round (R) and yellow (Y) seeds is crossed with another homozygous plant having wrinkled (r) and green (y) seeds. Answer the following questions:
- Give the genotype of the F1 generation.
- Mention the phenotype of the F1 offspring.
- Give the possible combinations of gametes that can be obtained from F1 hybrids.
- Give the dihybrid phenotypic ratio and the phenotype of the offspring of the F2 generation when two plants of F1 generation are crossed.
- Name and state the law which explains the dihybrid phenotypic ratio.
