Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Mention the different ways by which the population density of different species can be measured.
उत्तर
The population density of different species can be measured by:
(1) Quadrat method: It is a method that involves the use of a square of particular dimensions to measure the number of organisms.
Example: The number of Parthenium plants in a given area can be measured using the quadrat method.
(2) Direct observation: It involves the counting of organisms in the given area.
Example: In order to determine the number of bacteria growing in a Petri dish, their colonies are counted.
(3) Indirect method: In this method, there is no need to count the organisms individually.
Example: The number of fishes caught per trap gives the measure of their total density in a given water body.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Study the graph given below and answer the questions that follow :
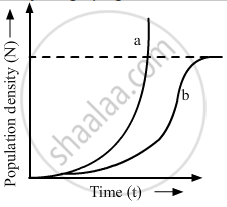
(i) Write the status of food and space in the curves (a) and (b).
(ii) In the absence of predators, which one of the two curves would appropriately depict the prey population?
(iii) Time has been shown on X-axis and there is a parallel dotted line above it. Give the significance of this dotted line
Give an account of population regulation.
The phenomenal and rapid increase of population in a short period is called ______.
Population having large number of postreproductive and small number of prereproductive age group is called
`"dN"/"dt" = "rN" (("K"- "N")/"K")` in logistic growth "K" represents:
What parameters are used for tiger census in our country’s national parks and sanctuaries?
The density of a population in a habitat per unit area is measured in different units. Write the unit of measurement against the following:
Fish
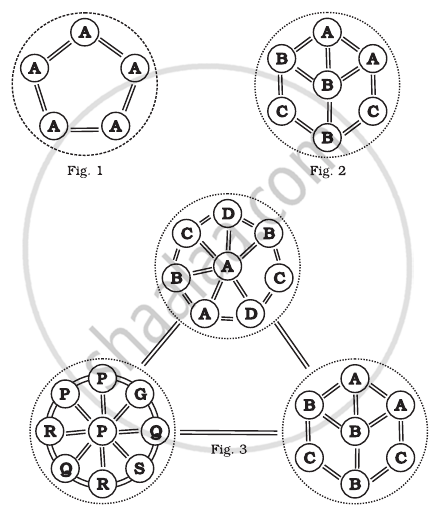
Comment on the following figures: 1, 2 and 3:
A, B, C. D, G, P, Q, R, S are species
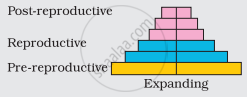
Identify the type of pyramid given above. Write the identifying feature on the basis of which you identified it.
With the help of neatly labelled diagrams, explain the different types of age pyramids of human population.
