Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Mention the various energy losses in a transformer.
उत्तर
Energy losses in a transformer: Transformers do not have any moving parts so that its efficiency is much higher than that of rotating machines like generators and motors. But there are many factors which lead to energy loss in a transformer.
- Core loss or Iron loss:
This loss takes place in the transformer core. Hysteresis loss and eddy current loss are known as core loss or Iron loss. When the transformer core is magnetized and demagnetized repeatedly by the alternating voltage applied across primary coil, hysteresis takes place due to which some energy is lost in the form of heat.
Hysteresis loss is minimized by using steel of high silicon content in making transformer core. Alternating magnetic flux in the core induces eddy currents in it. Therefore there is energy loss due to the flow of eddy current, called eddy current loss which is minimized by using very thin laminations of the transformer core. - Copper loss:
Transformer windings have electrical resistance. When an electric current flows through them, some amount of energy is dissipated due to Joule heating. This energy loss is called copper loss which is minimized by using wires of larger diameter. - Flux leakage:
Flux leakage happens when the magnetic lines of primary coil arc not completely linked with secondary coil. Energy loss due to this flux leakage is minimized by winding coils one over the other.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Write the function of a transformer.
State two factors on which the magnitude of induced e.m.f. depend.
The following diagram in Fig. 10.44 shows a coil X connected to a sensitive centre –zero galvanometer G and a coil P connected to a battery through a switch S.
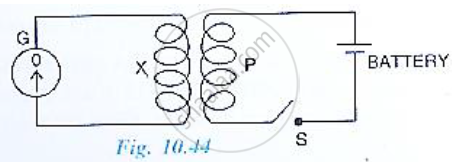
(a) Describe the observation when the switch S is (i) closed suddenly, (ii) then kept closed, (iii) finally opened.
(b) Name and state the law which explains the above observations.
Given the input current 15 A and the input voltage of 100 V for a step-up transformer having 90% efficiency, find the output power and the voltage in the secondary if the output current is 3 A.
Can a transformer be used with direct current source? Give reason.
The power supply to the primary coil of a transformer is 200 W. Find
(i) Current in primary coil if the e.m.f. supply to it is equal to 220V.
(ii) The number of turns in the primary coil is equal to 80 and that in secondary is 800. What is the transformation ratio?
(iii) Name the type of transformer.
(iv) What will be the output voltage?
(v) What is the current in the secondary coil for an ideal transformer?
(vi) What is the output power?
(vii) Is output and input power equal?
(viii) Compare the current flowing in a secondary coil and in a primary coil.
The primary coil of a transformer has 200 turns while the secondary coil has 1000 turns. What type of transformer is this? if the input voltage is 10V, what will be the output voltage?
The primary of a transformer has 40 turns and works on 100 V and 100 W. Find a number of turns in the secondary to step up the voltage to 400 V. Also calculate the current in the secondary and primary.
In a transformer, the number of turns in the primary and the secondary are 410 and 1230 respectively. If the current in primary is 6A, then that in the secondary coil is
Read the following paragraph and answer the question:

Long distance power transmissions
The large-scale transmission and distribution of electrical energy over long distances is done with the use of transformers. The voltage output of the generator is stepped up. It is then transmitted over long distances to an area sub-station near the consumers. There the voltage is stepped down. It is further stepped down at distributing sub-stations and utility poles before a power supply of 240 V reaches our homes.
Which of the following statement is true?
