Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Name the three classes of levers and state how are they distinguished. Give two examples of each class.
उत्तर
Three classes of levers are:
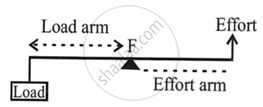
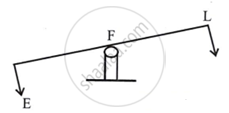
(a) Class I levers or first-order levers:
Examples are:
 |
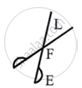 |
| See Saw | Scissors |
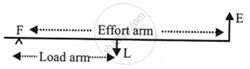
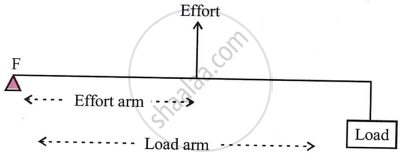
Between the effort and the load is the fulcrum.
[Ratio of M.A. and V.R.] for levers in this class can be any value between one and one, either more or less than one. They can multiply forces.
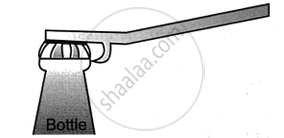
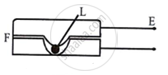
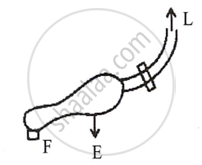
(b) Class II levers or second-order levers:
Examples are -
 |
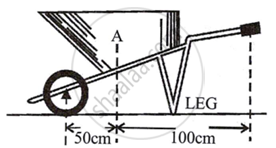 |
| Lemon squeezer | Wheel Barrow |
Between effort and fulcrum is load, with the effort arm always longer than the arm. These levers' M.A. and V.R. are always greater than 1.
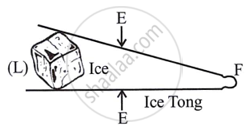
(c) Class III levers, or third-order levers:
Examples are
 |
 |
| Plucker or Fire Tong, (Sugar Tongs) |
Foot Treadle |
Always place effort between fulcrum and load. The effort arm is always shorter than the load arm. These levers' M.A. and V.R. are consistently less than 1.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Name the class to which the following lever belong:
a lemon squeezer
State three differences between the three classes of levers.
Answer the following.
Name the simplest of all types of machines.
Answer the following.
State the principle of levers.
Answer the following in short.
Using a suitable example, describe how a machine acts as a force multiplier.
Both a pair of scissors and a pair of pliers belong to the same class of levers. Name the class of lever. Which one has the mechanical advantage less than 1?
Explain why scissors for cutting cloth may have blades longer than the handles, but shears for cutting metals have short blades and long handles.
Classify the things below.
| Sl. No | Examples | Class of Lever |
| 1. | Spade | |
| 2. | Seesaw | |
| 3. | Wheel barrow | |
| 4. | Plier | |
| 5. | Nail cutter |
Lemon juicer belongs to which type of lever? Why?
Name the class of the lever shown in the picture below: