Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Observe the graph given below.
|
The graph represents inter-specific interaction between two species of Paramecia competing for the same resource in a culture medium. Paramecium caudatum and Paramecium aurelia were grown in separate cultures as well as in mixed cultures. It was found that each species grew in numbers according to the logistic equation.
|
a) Which species is competitively superior? Support it with the data provided in the graph.
b) State the underlying principle for the above result and name the scientist associated with this principle.
c) Explain the mechanism in which two or more species competing with each other can co-exist.
OR
Graphs A and B shown below depict interaction of two species. Which graph indicates Mutualism? Give reason.
 |
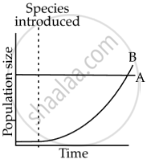 |
| A | B |
उत्तर
a) P. aurelia species is competitively superior P. aurelia grows in numbers more quickly than P. caudatum and shows more individuals in the same volume of culture/100 Paramecia aurelia in 6 days whereas 60 P. caudatum in 8 days.
b) Competitive Exclusion Principle’ which states that two closely related species competing for the same resources cannot co-exist indefinitely and the competitively inferior one will be eliminated. G.F. Gause.
c) One such mechanism is ‘resource partitioning’. If two species compete for the same resource, they could avoid competition by choosing different times for feeding or different foraging patterns, to avoid competition and co-exist due to behavioural differences in their foraging activities.
OR
Graph A - As both species grow simultaneously.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Which day is observed as ‘World Environment Day’?
State Gause’s Competitive Exclusion Principle.
Give one example of Interspecific competition.
What is population ecology?
What is ESS?
Predation and parasitism are which type of interactions?
In the given picture, identify the type of interspecific interaction.

What is brood parasitism? Explain with the help of an example.
Give one example for the following:
An organism which can conform
Write the observations made at the end of Connell's field, experiment on barnacles on the rocky sea coasts of Scotland.

