Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
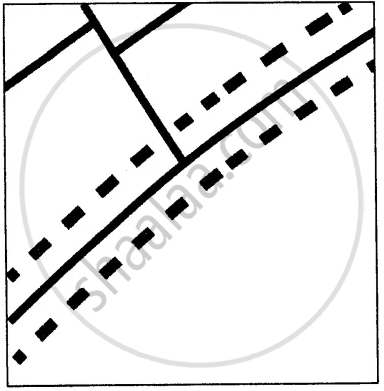
Picture study.

Write two characteristics of this type of settlement.
उत्तर
Linear settlements are those settlements that develop in a line. Houses, shops, dhaba’s, petrol pumps and garages develop along the sides of the roads, railway lines or river banks. Gradually, these linear settlements grow in size. These settlements gradually develop into trading centers.
Examples:
- If such a settlement is near a railway track, and over a period of time, a need for a railway station is felt, then it becomes a railway stop.
- When located on main roads, such settlements become important stops for travellers as dhaba’s, tyre and car repairing shops and petrol pumps open up.
- On rivers and coasts, they become places where boats can unload goods and passengers.
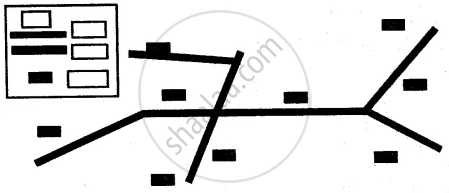
Scattered settlements are also known as dispersed settlements. Houses or huts in this type of settlement are far apart from one another. On map, such settlement is indicated by long distances between houses. Such areas show sparse population and the absence of proper roads. Houses or huts are usually connected by cart tracks or paths. Cattle rearing is common as each household has cattle that is allowed to graze in the open fields. The land is not very fertile to support big populations.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
How can transport and communication of an area be inferred directly from a topographical sheet?
Explain temporary settlements.
Explain permanent settlements.
Compare Nucleated settlement and scattered settlement.
Fill in the blanks
______ are groups of houses where people live, such as villages or towns.
Fill in the blanks
Tents and huts are the most common forms of shelter in ______ settlements.
Fill in the blanks
______ settlement develop in a line on either side of a road or a railway track.
Fill in the blanks
The grid on the ______ corner of a topographical map is always the reference point or the starting point.
Himalayas have dispersed settlement.
______ settlements are found in the Thar desert of Rajasthan.
