Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Proteins are found to have two different types of secondary structures viz. α-helix and β-pleated sheet structure. α-helix structure of protein is stabilised by:
विकल्प
Peptide bonds
van der Waals forces
Hydrogen bonds
Dipole-dipole interactions
उत्तर
Hydrogen bonds
Explanation:
These structures arise due to the regular folding of the backbone of the polypeptide chain due to hydrogen bonding between > C – O and N – H – group of the peptide bond.
α-helix is one of the most common ways in which a polypeptide chain forms all possible hydrogen bonds by twisting into a right-handed screw (helix) with the –NH group of each amino acid residue hydrogen-bonded to > C = O of an adjacent turn of helix.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Differentiate between the following :
Peptide linkage and Glycosidic linkage
Which of the following biomolecules is insoluble in water?
Which functional group participates in disulphide bond formation in proteins?
Which of the following statement is correct:
Optical rotations of some compounds along with their structures are given below which of them have D configuration.
| (I) | 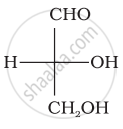 |
| (II) | 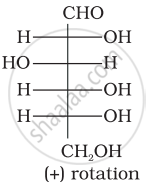 |
| (III) | 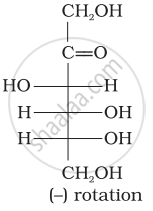 |
Which of the following are purine bases?
(i) Guanine
(ii) Adenine
(iii) Thymine
(iv) Uracil
Which moieties of nucleosides are involved in the formation of phosphodiester linkages present in dinucleotides? What does the word diester in the name of linkage indicate? Which acid is involved in the formation of this linkage?
Each polypeptide in a protein has amino acids linked with each other in a specific sequence. This sequence of amino acids is said to be ______.
Presence of disulphide link gives rise to which structure of protein?
Proteins are polymers of ______.
